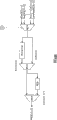CN100517215C - 用于无线系统中定时及事件处理的方法和装置 - Google Patents
用于无线系统中定时及事件处理的方法和装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100517215C CN100517215C CNB028169700A CN02816970A CN100517215C CN 100517215 C CN100517215 C CN 100517215C CN B028169700 A CNB028169700 A CN B028169700A CN 02816970 A CN02816970 A CN 02816970A CN 100517215 C CN100517215 C CN 100517215C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- clock
- timing
- instruction
- signal
- digital baseband
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 title claims description 16
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 15
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 51
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 24
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 17
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 14
- 108091006146 Channels Proteins 0.000 description 12
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 101000885321 Homo sapiens Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102100039758 Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000005059 dormancy Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- GOLXNESZZPUPJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N spiromesifen Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=CC(C)=C1C(C(O1)=O)=C(OC(=O)CC(C)(C)C)C11CCCC1 GOLXNESZZPUPJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 102100024362 Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 7 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 101000832771 Homo sapiens Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 7 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007616 round robin method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007958 sleep Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036962 time dependent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010792 warming Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/36—Preventing errors by testing or debugging software
- G06F11/362—Software debugging
- G06F11/3636—Software debugging by tracing the execution of the program
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/04—Generating or distributing clock signals or signals derived directly therefrom
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/04—Generating or distributing clock signals or signals derived directly therefrom
- G06F1/08—Clock generators with changeable or programmable clock frequency
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/3237—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by disabling clock generation or distribution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/324—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by lowering clock frequency
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/3287—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by switching off individual functional units in the computer system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/3296—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by lowering the supply or operating voltage
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0806—Multiuser, multiprocessor or multiprocessing cache systems
- G06F12/0842—Multiuser, multiprocessor or multiprocessing cache systems for multiprocessing or multitasking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/14—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer
- G06F13/20—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to input/output bus
- G06F13/28—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to input/output bus using burst mode transfer, e.g. direct memory access DMA, cycle steal
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/38—Information transfer, e.g. on bus
- G06F13/382—Information transfer, e.g. on bus using universal interface adapter
- G06F13/385—Information transfer, e.g. on bus using universal interface adapter for adaptation of a particular data processing system to different peripheral devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/30—Arrangements for executing machine instructions, e.g. instruction decode
- G06F9/38—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline, look ahead
- G06F9/3836—Instruction issuing, e.g. dynamic instruction scheduling or out of order instruction execution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/30—Arrangements for executing machine instructions, e.g. instruction decode
- G06F9/38—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline, look ahead
- G06F9/3836—Instruction issuing, e.g. dynamic instruction scheduling or out of order instruction execution
- G06F9/3851—Instruction issuing, e.g. dynamic instruction scheduling or out of order instruction execution from multiple instruction streams, e.g. multistreaming
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/30—Arrangements for executing machine instructions, e.g. instruction decode
- G06F9/38—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline, look ahead
- G06F9/3867—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline, look ahead using instruction pipelines
- G06F9/3869—Implementation aspects, e.g. pipeline latches; pipeline synchronisation and clocking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/48—Program initiating; Program switching, e.g. by interrupt
- G06F9/4806—Task transfer initiation or dispatching
- G06F9/4843—Task transfer initiation or dispatching by program, e.g. task dispatcher, supervisor, operating system
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03L—AUTOMATIC CONTROL, STARTING, SYNCHRONISATION, OR STABILISATION OF GENERATORS OF ELECTRONIC OSCILLATIONS OR PULSES
- H03L7/00—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation
- H03L7/06—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation using a reference signal applied to a frequency- or phase-locked loop
- H03L7/08—Details of the phase-locked loop
- H03L7/0802—Details of the phase-locked loop the loop being adapted for reducing power consumption
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03L—AUTOMATIC CONTROL, STARTING, SYNCHRONISATION, OR STABILISATION OF GENERATORS OF ELECTRONIC OSCILLATIONS OR PULSES
- H03L7/00—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation
- H03L7/06—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation using a reference signal applied to a frequency- or phase-locked loop
- H03L7/16—Indirect frequency synthesis, i.e. generating a desired one of a number of predetermined frequencies using a frequency- or phase-locked loop
- H03L7/18—Indirect frequency synthesis, i.e. generating a desired one of a number of predetermined frequencies using a frequency- or phase-locked loop using a frequency divider or counter in the loop
- H03L7/183—Indirect frequency synthesis, i.e. generating a desired one of a number of predetermined frequencies using a frequency- or phase-locked loop using a frequency divider or counter in the loop a time difference being used for locking the loop, the counter counting between fixed numbers or the frequency divider dividing by a fixed number
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0844—Multiple simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous cache accessing
- G06F12/0855—Overlapped cache accessing, e.g. pipeline
- G06F12/0859—Overlapped cache accessing, e.g. pipeline with reload from main memory
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2213/00—Indexing scheme relating to interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F2213/38—Universal adapter
- G06F2213/3814—Wireless link with a computer system port
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03L—AUTOMATIC CONTROL, STARTING, SYNCHRONISATION, OR STABILISATION OF GENERATORS OF ELECTRONIC OSCILLATIONS OR PULSES
- H03L7/00—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation
- H03L7/06—Automatic control of frequency or phase; Synchronisation using a reference signal applied to a frequency- or phase-locked loop
- H03L7/08—Details of the phase-locked loop
- H03L7/085—Details of the phase-locked loop concerning mainly the frequency- or phase-detection arrangement including the filtering or amplification of its output signal
- H03L7/095—Details of the phase-locked loop concerning mainly the frequency- or phase-detection arrangement including the filtering or amplification of its output signal using a lock detector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/02—Terminal devices
- H04W88/06—Terminal devices adapted for operation in multiple networks or having at least two operational modes, e.g. multi-mode terminals
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/50—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wire-line communication networks, e.g. low power modes or reduced link rate
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S331/00—Oscillators
- Y10S331/02—Phase locked loop having lock indicating or detecting means
Abstract
一种用于与不同的无线系统同时操作的数字基带处理器。数字基带处理器包括至少一个主处理器,用于执行第一指令序列中的指令;和定时及事件处理器,由数字信号处理器和微控制器控制,用于执行定时敏感性指令。定时及事件处理器包括:两个或多个指令序列发生器,用于执行定时敏感性指令线程;时基发生器,用于生成定时信号,该定时信号启动多个指令序列发生器中每一个中指令线程的执行,该时基发生器包括时钟校准电路;存储器,用于保持用于该两个或多个指令序列发生器的指令和数据;绝对计数器,用于计数校准后的低频时钟,并生成可编程的定时信号;I/O冲突裁决器,解决由该两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的输出中的冲突,以及响应冲突而产生异常。
Description
相关申请
本申请以2001年8月29日提交的申请号为60/315,655的临时申请为在先申请,并将其全部合并入本发明作为参考。
技术领域
本发明涉及无线通信,特别是无线系统中的定时及事件处理。
背景技术
随着无线通信网络的迅速发展,经常建立新的无线通信标准来代替旧的废弃的标准。然而,经常要花费时间在广泛的物理领域实现基于新标准的新无线网络。因此,人们常希望有既能和新无线网络通信又能和现存无线网络通信的无线终端。此外,随着无线计算机数据网络的迅速发展,人们常希望有能够和这些网络通信的无线终端,以允许用户浏览因特网或者收发电子邮件。此外,和不同的无线系统同时通信是有用的,这样用户可以例如在无线数据网络上查看电子邮件,同时在2G无线网络上进行语音电话呼叫。
这样的无线系统常使用不同的时基。例如2G GSM网络使用帧具有4.615毫秒的持续时间,并被分割为8时隙的时基。而3G WCDMA网络使用帧具有10毫秒的持续时间,并被分割为15时隙的时基。无论移动终端是与一个无线系统一起操作还是同时与两个或更多无线系统一起操作,移动终端中的事件必须精确定时并相对于每一个无线系统同步。
此外,为了维持便携性,无线终端一般由电池供电,其中在再充电之间的时间是最大电流(current drawn)的反函数。因为期望允许用户在再充电之间尽可能长时间操作无线终端,所以电源管理是重要的考虑因素。
发明内容
根据本发明的第一方面,提供一种数字基带处理器。该数字基带处理器包括至少一个主处理器,用于执行第一指令序列中的指令;和定时及事件处理器,连接至主处理器,用于执行第二指令序列中的定时敏感性指令。定时及事件处理器包括:两个或多个指令序列发生器,用于执行第二指令序列的线程;存储器,用于保持用于所述两个或多个指令序列发生器的指令和数据;时基发生器,用于产生定时信号,该定时信号用于使两个或多个指令序列发生器中每一个中的指令开始执行,其中,所述时基发生器包括时钟校准电路,用于根据相对稳定的高频时钟来校准相对不稳定的低频时钟,并生成校准后的低频时钟;绝对计数器,用于计数校准后的低频时钟,并生成可编程的所述定时信号;I/O冲突裁决器,用于解决由所述两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的输出中的冲突,以及响应冲突而产生异常。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种数字基带处理器,用于与不同无线系统同时操作。该数字基带处理器包括数字信号处理器,用于执行数字信号处理器指令;微控制器,用于执行微控制器指令;和定时及事件处理器,由数字信号处理器和微处理器控制,用于执行定时敏感性指令。定时及事件处理器包括多个指令序列发生器,用于执行定时敏感性指令线程;存储器,用于保持用于所述多个指令序列发生器的指令和数据;时基发生器,用于产生定时信号,该定时信号用于使两个或多个指令序列发生器中每一个中的指令开始执行,其中,所述时基发生器包括时钟校准电路,用于根据相对稳定的高频时钟来校准相对不稳定的低频时钟,并生成校准后的低频时钟;绝对计数器,用于计数校准后的低频时钟,并生成可编程的所述定时信号;I/O冲突裁决器,用于解决由所述两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的输出中的冲突,以及响应冲突而产生异常。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种用于产生定时信号的方法,该定时信号用于操作具有无线系统时基的无线系统中的无线终端。该方法包括产生校准后的慢时钟;通过计数校准后的慢时钟而产生绝对时间值,以提供统一的时基;和定时无线系统中的事件,这基于独立于无线系统时基的统一时基的绝对时间值。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种用于产生校准后的时钟的方法。该方法包括接收自由运行的快时钟;接收自由运行的慢时钟;修正自由运行慢时钟以提供校准后的慢时钟,该慢时钟与快时钟具有规定的关系;和提供相位补偿信号,该信号代表校准后的慢时钟中的相位误差。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种用于产生校准后的时钟的方法。该方法包括接收自由运行的快时钟;接收自由运行的慢时钟;规定快时钟和校准后的慢时钟之间的关系;计数所选择数量的自由运行慢时钟周期中的快时钟周期的数量,以提供比较值;基于快时钟和校准后的慢时钟之间规定的关系和比较值,从自由运行慢时钟中除去周期,以提供校准后的慢时钟;和提供相位补偿信号,该信号代表校准后的慢时钟中的相位误差。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种用于在基带处理器中执行DMA传送的方法。该方法包括在数字信号处理器内核中执行计算;在定时及事件处理器中生成定时信号;响应来自数字信号处理器的请求以及响应来自定时及事件处理器的定时信号,执行DMA传送,以提供定时的DMA传送。
根据本发明的又一方面,提供一种用于无线应用的基带处理器。该基带处理器包括数字信号处理器内核,用于执行数字信号计算;定时及事件处理器,连接至所述数字信号处理器内核,用于执行定时敏感性操作,所述定时及事件处理器包括时基发生器,用于产生定时信号,和DMA控制电路,用于启动DMA请求,以响应来自数字信号处理器内核的指令和来自时基发生器的定时信号;和DMA控制器,用于执行DMA请求,以提供定时的DMA传送。
附图说明
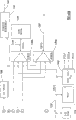
图1是根据本发明一实施例的通信处理器的框图;
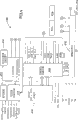
图2是根据本发明一实施例的图1通信处理器中的定时及事件处理器的框图;
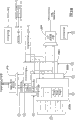
图3是根据本发明一实施例的图2定时及事件处理器中的序列发生器的框图;
图4是根据本发明一实施例的适用于序列发生器的指令格式的例子。
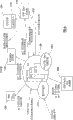
图5是用于说明根据本发明一实施例的定时及事件处理器的功能的图。
图6是根据本发明一实施例的直接存储器存取控制器与定时及事件处理器之间接口的框图;
图7是用于说明根据本发明一实施例的利用定时及事件处理器进行直接存储器存取的方法的例子的框图。
图8是根据本发明一实施例的与定时及事件处理器连接的外部总线的框图;
图9A是根据本发明一实施例的N分时器的例子的框图;
图9B是表示根据本发明一实施例的由N分时器生成的校准后的时钟和相位补偿的示意图;
图10是根据本发明一实施例的绝对计数器和可配置的周期触发脉冲发生器的框图;
图11A是根据本发明一实施例的快照有限态机器的框图;
图11B是根据本发明一实施例的图11A中快照有限态机器的操作的流程图;
图12是根据本发明一实施例的图2中定时及事件处理器中时钟和电源控制模块的框图;
图13A是根据本发明一实施例的时钟产生模块的框图;
图13B是根据本发明一实施例的时钟分配模块的示意图;
图14A是根据本发明一实施例的时钟门控模块的示意图;
图14B是用于说明根据本发明一实施例的图14A中所示的寄存器的内容的表;
图15是用于说明根据本发明一实施例的振荡器断电需求的框图。
具体实施方式
无线终端可以包括无线电单元、数字基带处理器、用户接口、和电池。基带处理器可以包括用于执行数字处理算法和其他复杂计算的数字信号处理器,和用于执行控制功能和相对简单计算的微控制器。由无线终端中的基带处理器执行的许多任务都需要精确定时。例如,在无线通信网络中,预定无线信道中的动作以规定的精度在指定的时间发生。专用的定时及事件处理器(TEP)可以用来达到这样的定时精度。例如,TEP可以负责产生定时信号、调度事件、产生至处理器的中断、启动其他模块中的操作、为芯片外电路产生控制信号,例如无线电单元。TEP可以与数字信号处理器、微控制器和基带控制器的其他元件协同工作,来控制无线终端中的所有定时和事件。
有时会期望同时与若干不同的无线系统进行通信。例如,通信处理器与诸如蓝牙网络的无线数据网络进行通信,以监控用户的新电子邮件,同时监控无线CDMA网络的寻呼信道,以发现新的语音电话呼叫。通常,与通信处理器通信的不同的无线系统利用不同的时基。TEP可以利用共同的基准时钟作为时基来为无线系统安排事件,从而为与通信处理器通信的任何无线系统安排事件。
图1表示根据本发明一个实施例的基带通信处理器100的框图。图1所示的处理器包括两个处理内核。数字信号处理器(DSP)内核102可以用来执行通信处理器100的数字信号处理功能,比如与单元搜索、信号的相关、信道编码和解码相关的处理。许多其他的信号处理功能可以由DSP内核102执行。适用于本发明实施例的DSP内核的一例在2000年11月16日公开的PCT公开号为WO 00/687783中公开。但是,应该理解可以使用许多其他类型的数字信号处理器,本发明不限定于任何特定的数字信号处理器。微控制器单元(MCU)104处理内核可以用来执行用于通信处理器100的控制码,比如协议堆栈指令的执行。市面上可获得的适用于本发明的MCU的一例是ARM7TDMI内核,由Advanced RISC Machine,Ltd.出售。但是,应该理解可以使用许多其他类型的微控制器,本发明不限定于任何特定的微控制器。
通信处理器100也包括系统存储器106。系统存储器106可以是静态随机存储器(SRAM)、或任何其他类型的易失性存储器或非易失性存储器,比如动态随机存储器(DRAM)、同步动态随机存储器(SDRAM)或铁电随机存储器(FRAM)。DSP内核102和MCU104利用共同的存储映像表。因此,这些处理器可以共享对系统存储器106的访问并可以通过系统存储器106互相通信。
图1所示的每一个元件可以由单一集成电路和多个集成电路实现。在一些实施例中,将整个通信处理器100制造在单一芯片上。应该理解本发明不限定于这方面。
直接存储器存取(DMA)控制器134和136用来促进通信处理器100中的数据传送。DMA控制器134和136允许在设备与存储器(例如,系统存储器106)之间直接传送存储内容而不受处理器干涉。可以为设备分配DMA通道以允许这些设备请求DMA传送。通道配置由DSP内核102与MCU 104确定。尽管两个处理器都可以访问每一个DMA通道,但是可以由DSP内核102控制一个通道组的通道配置,由MCU内核104控制另一个通道组的通道配置。同样,DMA控制器134可以控制由DSP内核102配置的通道的DMA传送,而DMA控制器136可以控制由MCU 104配置的通道的DMA传送。
DSP内核102可以包括级别1(L1)指令高速缓存144和L1数据高速缓存146,用来当访问存储数据时提供较低的等待时间。DSP内核102可以具有两条连接至L1数据高速缓存146的数据总线、一条连接至L1指令高速缓存144的指令总线、和一条连接至高速缓存144和146的DMA总线。级别2(L2)存储器148可以是由DSP内核102使用的专用的SRAM。存储器148可以被DMA控制器134访问。存储器148也可以被MCU 104、DMA控制器136、和外部应用处理器接口(EAPI)142访问。
系统总线接口单元(SBIU)132执行总线桥接功能。例如,SBIU132可以作为非对称交叉开关,用来将来自DSP内核102、DMA控制器134、MCU 104、DMA控制器136、和外部应用处理器接口142的请求分配到适当的系统资源,比如L1高速缓存144、L1高速缓存146、L2存储器148、和其他系统资源。SBIU 132允许各种总线之间并行和同时的数据传送。
人机接口(MMI)模块150提供通信处理器100的硬件用户接口并可以通过PBUS总线128访问。MMI 150模块可以包括通信处理器100的通用输入输出(GPIO)引脚的接口。这些引脚可以用作各种用途,包括接口无线电单元和其他外部设备。其他MMI模块可以包括显示屏接口、串行端口接口、通用异步收发器接口(UART)、USB接口、和包含嵌入了通信处理器100的无线终端的唯一序列号的用户标识模块(SIM)。许多其他接口模块可以包括在MMI 150中。
内务处理模块执行各种用于通信处理器152的内务处理功能,并可以通过PBUS总线128访问。这种功能包括当通信处理器中发生软件死锁时超时并产生复位的监视时钟(WDT),用于触发通用定时功能的通用时钟,和用于管理至DSP内核102和MCU 104的中断的IRQ控制器。
无线系统模块154提供外部无线系统元件与通信处理器100的接口并可以通过PBUS总线128访问。例如,无线系统模块154可以包括作为至模拟基带芯片的控制串行端口的CS端口,和至频率合成器的接口。
DSP外围设备与DSP内核102一起执行各种数字信号处理功能并可以通过DPBUS总线110访问。DSP外围设备可以包括,例如协处理器接口162、BS端口164、旗标I/O 166、高速记录器168、加密引擎170、和DSP IRQ控制器172。
利用一条或多条总线,数据可以在通信处理器的各种元件之间和通信处理器与芯片外设备之间传送。每条总线都可以是并行或串行总线。每条总线都可以是不定向的或定向的。此外,每条总线都可以包括地址总线、数据总线和控制总线中的任何一个。图1所示的通信处理器100的总线配置包括多个总线系统。下面大概介绍每一个总线系统的功能。对本领域技术人员而言,可以在本发明的主旨和范围内对图1所示的总线配置进行许多变更、修改、和改进。
SYSL2总线108连接在SBIU 132与L2存储器148接口之间。存储器144在MCU 104、系统DMA控制器136、DSP DMA控制器134、和DSP 102之间共享。DPBUS总线110是DSP外围设备总线和各种DSP外围设备的接口,外围设备比如可以是基带串行端口的BS端口164、协处理器接口162、旗标I/O 166、高速记录器168、加密引擎170、和DSP IRQ控制器172。MCU 104、系统DMA控制器136、和DSP DMA控制器134之间共享对DPBUS总线110的访问。DSP内核102也可以通过SBIU 132访问DPBUS。DSPBUS总线112是DSP内核102至PBUS总线128、系统存储器106、和EBUS总线100的接口。DABUS总线114作为DSP DMA控制器至SBIU 132的接口。DMABUS总线116是系统DMA控制器136与PBUS总线128、RBUS总线118、和EBUS总线120上的资源之间的接口。RBUS总线118是至系统存储器106的接口。MCU 104、系统DMA控制器136、DSP DMA控制器134、和DSP内核102之间共享对RBUS总线118的访问。EBUS总线120作为至位于通信处理器100外部的闪速存储器和SRAM的接口。SBUS总线122是MCU 104的主系统总线。EAPI总线124作为从通信处理器100外部的应用处理器至通信处理器100的资源的接口。EABUS总线140是EAPI 142与通信处理器100外部的应用处理器之间的接口。应该理解并不是必须提供外部应用处理器。CBUS总线126是至外部协处理器的接口。PBUS总线128是外围设备总线,将无线系统外围设备154、内务外围设备152、和MMI外围设备150连接至MCU 104、系统DMA控制器136、DSP DMA控制器134、和DSP内核102。
因为对某些总线的访问被多个元件共享,比如PBUS总线128和RBUS总线118,所以提供总线仲裁器130a、130b和130c来管理对这些总线的访问。
通信处理器100包括定时及事件处理器(TEP)138,用来为通信处理器100安排事件。这些事件可以包括,例如,I/O引脚的置位和清除、产生至DSP内核102和MCU 104的中断、初始化TEP 138和通信处理器100其他模块之间的DMA存储内容传送。TEP 138经由DPBUS总线110连接至通信处理器100的其他模块,也连接至DSPDMA控制器134和DSP IRQ控制器172。
在TEP 138中,不同的无线系统时基被转换为不特定于任何无线系统的统一的时基。利用统一的时基,事件被安排为在绝对时间点触发。TEP 138产生校准后的慢时钟作为统一时基的基准,通过使用高精度的自由运行快时钟作为校准基准来获得校准后的慢时钟的长期稳定性。通过从自由运行慢时钟中除去时钟脉冲来产生被用作统一时基的时钟的校准后的慢时钟。这会产生相位误差,为了获得精确的定时信号,该误差被补偿。为自由运行慢时钟的每个时钟周期计算相位补偿。相位补偿表示为自由运行快时钟的时钟周期的数量,并与校准后的慢时钟一起使用,来提供精确定时。一个特征是即使切断自由运行快时钟,相位补偿值仍能保持。这些特征在下文详细论述。
图5是说明TEP 138功能的例子的示意图。TEP 138可以置位和清除GPIO引脚以控制与外部设备的接口。TEP 138也可以与系统DMA控制器136和DSP DMA控制器134通信来启用DMA通道。利用专用的DMA通道516,TEP 138也可以读和写任何存储映像位置,允许TEP 138与诸如无线系统154的其他模块通信,例如,使用频率合成器接口154a来对频率合成器编程。TEP 138可以与DSP和MCU IRQ控制器506接口来生成每一个处理内核的中断,通过接收来自TEP 138的中断,允许处理内核在不工作时进入空闲状态,在必要时退出空闲.状态。可以如下所述对TEP的所有功能进行精确定时和安排。
图2是根据本发明一个实施例的TEP结构138的例的框图。TEP138可以作为通信处理器100的定时及计划机构。在无线系统的操作中,所有无线电控制事件在预定的事件发生并需要精确定时。在通信处理器100动作之间的某些时间,特别是无线通信应用中,MCU 104和DSP内核102都不需要执行任何处理功能,可以进入空闲方式或“休眠”方式。在这种方式中,不需要为处理内核计时,因此允许振荡器断电。通信处理器100可以嵌入无线终端,由电池供电。通过在不需要时使处理器空闲或使振荡器断电而节约电能可以延长电池需要再次充电前的时间。然而,在处理内核空闲之前,它们可以指示给TEP 138它们需要再次启动的时间。
TEP 138可以包括多个序列发生器202a-202n,用来执行被TEP 138利用的指令以执行时间特定的动作。TEP 138也包括存储器206,该存储器可以是例如静态随机存储器(SRAM)。序列发生器202a-202n可以使用存储器206来存储编码和数据。存储器存取裁决器208处理来自序列发生器202a-202n和DPBUS总线110的存储器存取请求。DPBUS总线接口模块210提供系统时钟与TEP 138中DPBUS总线时钟域之间的桥接。下文对DPBUS总线接口模块201进行详细阐述。TEP138还包括时钟校准块212,可以用作TEP中统一时基的时钟校准。下文对时钟校准块212进行详细论述。TEP 138也可以包括被序列发生器202a-202n用来定时的绝对计数器214。下文对绝对计数器214进行详细论述。TEP 138可以包括I/O冲突裁决器204,用来解决从序列发生器202a-202n接收的冲突信号。下文对I/O冲突裁决器204进行详细论述。下文做详细论述的时钟和电源控制块216用来在可能时给系统时钟断电。
序列发生器202a-202n可以是处理器,比如RISC处理器,具有专用的指令系统并可以同时为多个无线系统提供定时。即,序列发生器202a-202n可以产生置位和清除GPIO引脚的信号、给DMA控制器发信号、为DSP内核102和MCU 104产生中断。序列发生器可以用来为每一个被同时支持的无线系统执行指令。为每一个无线系统提供两个或更多序列发生器可以提高性能。例如,在本发明的一个实施例中,可以为每一个同时被支持的系统提供两个序列发生器。在这种配置中,一个序列发生器执行指令的同时另一个序列发生器正在加载指令。应该理解单个序列发生器可以支持多个无线系统。单个序列发生器可以加载与两个不同的无线系统相关的指令。然而,使用单个序列发生器不能实现真正的并行性,因为执行和第一个无线系统相关的指令的时间与执行和第二个无线系统相关的指令的时间重叠。因为这些指令由单个序列发生器顺序执行,所以它们不能同时执行。然而,也应该理解不是必须为每一个无线系统使用两个序列发生器。每个无线系统可以使用一个序列发生器,或者使用三个或更多序列发生器。与无线系统的处理不相关的一个附加的序列发生器可以用来提供普通定时。例如,附加的序列发生器可以用来安排计时事件来更新无线终端的显示屏上的时钟。在一些实施例中,TEP 138包括为每个同时被支持的无线系统的两个序列发生器和一个附加的序列发生器。
使用多个序列发生器允许通信处理器100同时与多个不同的无线系统通信,而不管无线系统使用不同定时的事实。例如,无线终端监视GSM网络的寻呼信道,同时从无线LAN、蓝牙网络、或其他802.11b网络接收数据。同样,具备具有多个序列发生器的通信处理器的无线终端,一启动就同时执行2G GSM网络和3G WCDMA网络的单元搜索。
如上所述,TEP 138能够置位和清除GPIO引脚、启动DMA通道、产生中断、和执行时钟校准。然而,两个或多个序列发生器会声明冲突信号。例如,一个序列发生器声明置位一个特定I/O引脚的信号,而同时不同的序列发生器声明要清除同一个引脚的信号。如图2所示的I/O冲突裁决器204处理这种冲突。I/O冲突裁决器204包含解决冲突的规则。例如,一个规则可以是任何清除信号优先于置位信号。会产生异常来通知冲突的软件进程,并发送中断到处理内核。对于中断和DMA通道启动,会简单地结合冲突信号,例如使用逻辑或操作。
如图2所示的存储器,可以通过与DPBUS总线110连接的DPBUS总线接口210由处理器访问。根据本发明的一个实施例,存储器206是26比特宽,并且是多端口的,以允许同时被序列发生器202a-202n和DPBUS总线110访问。为存储器206提供的读和写端口的数量根据TEP 138中序列发生器的数量来选择。例如,为每一个序列发生器提供一个读端口和一个写端口。然而,大量的端口消耗芯片空间,并需要更多指令解码器。或者为每个序列发生器提供一个指令解码器。此外,不可能所有的序列发生器将在相同时钟周期访问存储器。因此,存储器206的读端口的数量可以根据同时被支持的无线系统的数量来选择。例如,为每个被支持的无线系统提供一个读端口。因为写访问发生的频率少于读访问,所以可以提供少于读端口的写端口。存储器206端口的数量可以根据任何标准选择,本发明不限定存储器206端口的数量。
如上所述,存储器访问裁决器208处理来自序列发生器202a-202n和DPBUS总线110的对存储器206的访问请求。存储器访问裁决器208也处理冲突,例如在访问请求多于读端口的情况下。存储器访问裁决器208例如通过基于循环法区分请求的优先顺序来处理这种情况。在这种循环法中,移回(shift-back)寄存器可以用来确定优先顺序。在一个实施例中,当存储器访问发生冲突时,寄存器移位。在另一个实施例中,在序列发生器的每一次存储器访问时,移回寄存器就移位。然而,应该理解可以使用许多其他解决请求冲突的方法。
DPBUS总线接口模块210在系统时钟和TEP 138中DPBUS总线时钟域之间提供桥接。DPBUS总线接口模块210也处理DPBUS总线110与内部TEP总线之间的16/32比特接口。
图8表示根据本发明一个实施例的DPBUS总线接口模块210的框图。如上所述,DPBUS总线接口模块210执行DPBUS总线时钟与系统时钟之间的时钟间同步。可以利用用于相互同步的联络信号分别控制每个时钟域。DPS协议FSM 802处理至DPBUS总线的联络信号。TEP访问FSM 804处理至内部TEP总线的联络信号。
图3是用于说明根据本发明一个实施例的序列发生器202a结构的框图。序列发生器202a可以是包括读取、解码、和执行阶段的流水线处理器。指令解码器328解码从多路复用器342接收的指令。指令读取自TEP 138的存储器206。在DSP内核102和MCU 104的控制下,序列发生器指令被加载到TEP 138的存储器206中。多路复用器342将与指令相关的数据送至寄存器326。寄存器326中存储的数据是读或变更操作中被写入的数据或者是从读操作得到的数据。序列发生器202a还包括与DMA控制器134和DMA控制器136接口的DMA控制模块348。序列发生器202a包括多个DMA寄存器(例如,302、304、306、308、310),用来配置DMA通道。序列发生器202a包括时钟预变换(pre-scale)模块346,用来产生时间脉冲信号以增加delta计时器336。序列发生器控制模块334处理序列发生器的全部操作,在下文进行详细论述。
图4表示由序列发生器202a-202n执行的指令的格式的例子。指令400包括用于识别指令类型的6比特操作码字段402。4比特数据字段404包括处理指令需要的数据。例如,用于置位通用输入输出(GPIO)引脚的指令包括用于识别要置位的GPIO引脚的数据域。扩展字段406作为数据字段404的8比特扩展可以选择地使用。如果与指令相关的数据超过4比特数据字段,可以使用扩展字段406保持溢出的部分。Delta时间字段408用来指示指令执行前的时间延迟。Delta时间字段408指示在前一个指令执行后和当前指令(即指令400)执行前要等待的时间。
由指令解码器328对指令解码后,图3所示的delta计时器336计时在指令的delta域中指示的等待时间段。当时间延迟达到了delta计时器336的时间,执行单元330将执行命令。基于delta计时器的指令执行允许序列发生器执行随时间变化的功能,即计划在特定时间发生的功能。例如,序列发生器可以向处理内核102和104(图1)产生定时中断以允许处理器不工作时进入空闲状态,并且产生定时中断以在适当的时间退出这种空闲状态。序列发生器指令可以控制引脚的置位从而控制外部设备,并可以给无线电单元加电或断电。序列发生器指令也可以在特定的时间启动DMA通道。
图3所示的时钟预变换模块346用来产生时间脉冲信号以增加delta计时器336。时钟预变换模块346执行系统时钟的时钟分割以产生时间脉冲信号。为了节约电能,期望尽可能地使用低频率,而仍能够为无线系统的操作提供充分的定时精度。因为时钟频率取决于无线系统的定时,时钟预变换模块346可以利用2至64之间的任何预变换值分割系统时钟。预变换值储存在寄存器314中。
表1给出了根据本发明一个实施例的序列发生器指令系统的例子。
表1
有时候必须同时置位或清除两个或更多I/O引脚。尽管序列发生器指令系统可以提供置位或清除I/O引脚的指令,但这些指令顺次扩展,不是同时的。同时置位或清除两个或更多I/O引脚,置位和清除指令同步到特定的信号。例如,如果需要同时置位引脚GPIOA和引脚GPIOB,序列发生器会将这些信号同步到GPSigA。然后,序列发生器首先执行置位引脚GPIOA的指令,接着是置位引脚GPIOB的指令。直到执行了切换GPSigA指令后,这些引脚才被真正置位,该指令使得两个引脚同时被置位。
当序列发生器执行LongWait指令时使用LongWait比较模块340。当给定数量的时间内序列发生器不执行序列发生器指令的时候,就执行LongWait指令。为了节省电能,LongWait指令允许系统时钟断电并允许序列发生器使用慢时钟来定时。
LongWait比较模块340将LongWait指令所指示的等待时间与绝对计数器214(图2)的值进行比较,下文进行详细论述。等待时间是24比特的值,于是需要使用8比特delta时间字段、8比特扩展字段、4比特数据字段、和6比特操作码的4比特。LongWait比较模块340接收来自24位绝对计数器214的输入,并将该值与LongWait指令的24比特等待时间进行比较。当值相匹配时,序列发生器执行接下来的指令。LongWait比较模块340也输出空闲信息,TEP 138的时钟和电源控制块216利用该信息来确定序列发生器是否正在执行LongWait指令,从而当所有序列发生器在空闲状态时给系统时钟断电。
如果振荡器已经关闭,PreAbs32寄存器338用来确定给振荡器加电的时间。PreAbs32寄存器指示给振荡器加电的绝对时间点,允许振荡器在当前正在执行的LongWait指令结束和下一个指令开始执行以前有充分的时间来稳定。
序列发生器控制模块334控制程序流程并处理序列发生器202a-202n的中断。序列发生器控制模块334根据程序计数寄存器322中的内容来请求来自存储器的指令。程序计数寄存器322保存下一个将被执行的指令的地址。序列发生器控制模块334通过线路344接收来自中断选择器332的中断,该中断选择器332从多个中断源中选择最高优先次序的中断请求。当接收到中断,寄存器316中的中断允许位被置位,并且中断向量的地址被加载到寄存器318。序列发生器跳转至寄存器318中中断向量的地址并从那里继续执行。
当序列发生器接收到硬复位或执行终止指令,序列发生器进入空闲状态。软复位被用来指示序列发生器读取第一条指令并开始执行指令。当序列发生器接收到软复位或中断,它将继续正常执行。如果序列发生器接收到软复位,序列发生器要跳转至并开始执行的地址保存在寄存器320中。如果序列发生器接收到中断,序列发生器要跳转至并开始执行的中断向量的地址保存在寄存器318中。
DMA寄存器302、304、306、308和310被序列发生器用来存储DMA通道配置信息。例如,这些寄存器存储源地址、目标地址、和若干要传送的字节。DMA控制模块348连接DSPDMA控制器134(图1)和系统DMA控制器136来初始化DMA传送。
图6表示TEP 138和DMA控制器134之间接口的例子。一个DMA通道由TEP 138专用而不能被其他资源利用。例如,尽管任何DMA通道都能使用,分配通道0被TEP使用。通过执行指令,序列发生器202a-202n利用固定的通道来启动DMA传送,例如表1的序列发生器指令系统中所示的DataMoveE指令。DataMoveE指令从DMA寄存器302、304、306、308、和310中得到DMA通道配置信息,并将该信息复制到DMA控制器134的内部RAM 604。若干序列发生器会同时请求访问专用的DMA通道。请求裁决器有限态机器(FSM)218处理这些同时的请求。例如,请求裁决器FSM 218使用循环优先权方法来允许序列发生器202a-202n有权使用DMA通道。当访问被允许后,DMA寄存器的值被复制到DMA控制器的存储器604,请求裁决器FSM218置位用于启动专用DMA通道的通道启动标志。当DMA传送结束后,DMA控制器134向请求裁决器FSM 218返回一个中断。此外,请求裁决器FSM 218在使用中会声明一个DRReqSysClk标志(未表示),以确保在DMA传送中系统时钟不会被断电。
图7示意地表示如以上关于图6的说明的TEP初始化DMA传送的例子。首先,TEP 138利用专用通道向DMA控制器134发送通道配置信息,并向DMA控制器134发送通道启动信息。DMA控制器134执行数据传送并向TEP 138发送中断以表示数据传送的结束。
图2所示的时钟校准单元212用来校准通信处理器100的慢时钟。通信处理器100从例如13MHz的系统时钟和例如32kHz的自由运行慢时钟接收时钟信号。如系统时钟那样的高频时钟用来给通信处理器100的处理内核计时,而慢时钟可以在处理内核处于空闲状态,并且不需要由高频时钟计时的时候用作计时控制,以节省电能。TEP138可以从慢时钟得到系统计时。由TEP 138处理的计时事件基于慢时钟的时间和与慢时钟周期相关的delta时间(在系统时钟周期中计数)。当不需要时,系统振荡器可以由通信处理器100的任何模块断电,当接下来预定的操作需要时,依靠慢时钟来给系统时钟加电。系统振荡器的断电在下文进行详细论述。
慢时钟没有高频系统时钟精确,并且对温度变化更敏感。因此,要校准慢时钟以保证期望的精确程度。可以利用系统时钟或通过无线电接收的无线系统的计时来校准慢时钟。如果利用系统时钟校准,在所选择数量的慢时钟周期之上计算系统时钟周期的数量。如果利用来自无线系统的计时来校准,在所选择数量的慢时钟周期之上计算无线系统时钟周期(通过无线电接收)的数量。
利用频率合成器或VCO校准慢时钟将消耗功率,为了节电,通过从自由运行慢时钟中除去时钟周期以提供校准后的慢时钟来校准慢时钟。即,选择比自由运行慢时钟的预期频率低的频率(例如,在32kHz慢时钟的情况下选择31kHz),并且通过从自由运行慢时钟信号中除去时钟脉冲来生成校准后的时钟信号。通过N分时器来调整自由运行慢时钟,它定期地从自由运行慢时钟中除去时钟周期。从自由运行慢时钟中除去时钟周期的时间段取决于规定的分数、系数值,和比较慢时钟和系统时钟而获得信息。例如,如果除去时钟周期的时间段是9个慢时钟周期,则每9个未校准的慢时钟周期会生成8个校准后的慢时钟周期。
然而,从自由运行慢时钟周期中除去时钟周期会将相位误差引入校准后的慢时钟。这种相位误差是由于校准后的慢时钟不是真正的周期的而引起的。例如,假定40kHz校准后的慢时钟是从自由运行50kHz时钟中生成。50kHz时钟每20μ秒具有一个上升沿。即,50kHz时钟在20μ秒、40μ秒、60μ秒、80μ秒、100μ秒、120μ秒等具有上升沿。40kHz校准后的慢时钟是通过定期除去周期而生成。因此,校准后的慢时钟将在20μ秒、40μ秒、60μ秒、100μ秒、120μ秒等具有上升沿。校准后的慢时钟达到40kHz的平均数,即每秒40,000时钟上升沿,但是与真正的40kHz时钟不同相。真正的40kHz时钟每25μ秒具有一个时钟上升沿。例如,真正的40kHz时钟将在25μ秒、50μ秒、75μ秒、100μ秒、125μ秒等具有上升沿。因此,校准后的40kHz时钟的上升沿与真正的40kHz时钟的上升沿发生在不同的时间,由于校准后的慢时钟与相同频率的真正的时钟之间的相位差异而采用相位补偿,下文将阐述。
图9A和9B分别表示根据本发明的一个实施例,带相位补偿的N分时器的实现和用于说明相位补偿的时序图。分数增加寄存器902存储快时钟周期与自由运行32kHz时钟周期的比率,并作为加法器904的一个输入。相位补偿寄存器906是用于累加加法器904的输出的累加器并作为模数操作器912的一个输入。模数寄存器908存储的值通过比较器914与相位补偿寄存器906中的上10位进行比较。比较器914作为与门910的输入并控制自由运行32kHz时钟是否通过门910。模数寄存器908是模数操作器912的第二个输入。模数操作器912计算模量,当比较器被置位时,该模量被用来增加相位补偿寄存器906。
当寄存器906中的值达到模数寄存器908中的值,比较器914的输出被置位,从而禁止门910的输出。可以看出,在每一个自由运行32kHz时钟周期,相位补偿的数量(即,寄存器906的值)被累积并线性增长。当累加器达到模数寄存器908,自由运行32kHz时钟周期输入被禁止,直到下一个时钟周期。然后相位补偿累加器由经模数操作器912计算的模量回绕(warp around)。
如上所述,除去时钟脉冲将相位误差引入校准后的时钟信号。相位误差的产生是由于图9B所示的已除去脉冲的校准后的慢时钟930具有与同频率的自由运行时钟不同时间发生的时钟沿。如图9B所示的波形932,相位误差伴随每一个慢时钟周期增加直到除去一个脉冲,然后归零。如果不进行相位补偿,这种相位误差将在无线系统中导致定时误差。通过利用校准后的慢时钟和代表相位误差的相位补偿信号,可以利用校准后的慢时钟获得精确的定时。
因此,当使用校准后的时钟信号驱动绝对计数器214的时候,通过利用相位补偿寄存器906中计算的相位补偿来补偿校准后的时钟信号中的相位误差。参考上文利用50kHz自由运行慢时钟和40kHz校准后的慢时钟而论述的例子,假定一个事件预定在40kHz时钟信号的第三个上升沿发生。如上所述,在真正的40kHz时钟中,第三个上升沿发生在75μ秒。而在校准后的40kHz时钟中,第三个上升沿发生在60μ秒。因此,校准后的慢时钟与真正的40kHz时钟不同相15μ秒。当校准后的慢时钟在60μ秒到达第三个上升沿时,在系统时钟周期中计算的15μ秒的进一步延迟在预定时间执行前被增加。如此,序列发生器补偿校准后的时钟信号的调整后的频率。
有时,由于例如温度的迅速变化,不能得到慢时钟的充分的稳定性。然而,仍然需要生成校准后的慢时钟信号,来驱动绝对计数器并为LongWait指令的执行定时。在这种情况下,可以使用系统时钟的频分。例如,分时器可以将系统时钟分割为校准后的慢时钟。
图2所示的绝对计数器214由校准后的慢时钟计时。图10更详细表示了绝对计数器214。在一个实施例中,绝对计数器214是24比特计数器,并且由正在执行LongWait指令的序列发生器202a-202n使用,来确定等待时间段何时期满。例如,序列发生器202a-202n将绝对计数器214的值与LongWait指令的等待时间段进行比较,来确定等待时间段何时期满。
提供两个周期性触发脉冲发生器1002和1004,可以用作各种用途,比如触发中断或者触发快照。快照是慢时钟相对于系统时钟的测量,或者慢时钟相对于通过无线电接收的无线系统的计时的测量,它们用作慢时钟的校准。快照包括计算给定的慢时钟周期数量中系统时钟周期的数量。
图11A和11B分别表示用于获得快照的框图和状态转移图。快照由多个不同的输入启动。例如,基于任何序列发生器的寄存器文件中的SeqCtrl寄存器312(图3)的置位比特,快照可以由绝对计数器的两个周期性的触发脉冲中的任何一个启动,或者由运行在两个处理内核的任何一个中的软件启动。
当启动快照时,校准信号被声明以防止系统时钟断电。接下来,快照FSM 1108进入准备状态1103,在该状态中它等待接收SysClkOk信号1110,表明系统时钟振荡器没有断电。当接收到SysClkOk信号1110,快照FSM 1108进入快照状态1105,在该状态中,在若干慢时钟周期时间段计算系统时钟周期的数量。在TCLR寄存器1112中规定慢时钟周期的数量,该数量可由软件配置。在TCLR寄存器1112中规定的慢时钟周期的数量已经被慢时钟周期计数器1114计数之后,产生中断并且快照FSM 1108进入回读状态1107。当快照FSM 1108在回读状态1107时,系统时钟周期计数器1116可由处理内核经由DPBUS总线接口210读取,以更新慢时钟的校准所需要的任何计数器。读计数器1116之后,快照FSM1108返回空闲状态1101。
图2表示了时钟和电源控制块216。当TEP 138的某些模块不使用时,为了省电可以关闭至这些模块的时钟信号。如果一个或多个序列发生器正在执行LongWait指令并且没有其他模块需要使用系统时钟,时钟和电源控制块216确定LongWait指令的持续时间是否充分以允许系统时钟断电。
图12是时钟和电源控制块216的框图。许多TEP模块需要使用系统时钟,比如存储器存取裁决器208和DMA请求裁决器218,它们可以分别通过信号1206和1208向时钟和电源控制块216指示需要系统时钟。外部源提供外部信号ReqSysClk 1210来向TEP指示一个或多个外部模块需要使用系统时钟。关于何时提供ReqSysClk信号的确定在下文详细论述。时钟校准模块在执行慢时钟校准时声明校准信号1212,并请求系统时钟维持激活。
每个序列发生器202a-202n通过置位复位触发器(SRFF)1218向时钟和电源控制块216指示需要系统时钟。SRFF 1218的Q输出是TEPReqSysClk信号1216。不需要系统时钟的每个序列发生器通过与门1222声明KillSysOsc信号。当没有序列发生器需要系统时钟时,SRFF1218进入复位状态,不声明信号1216。如果有任何序列发生器需要使用系统时钟,它通过或门1224声明一个重启系统振荡器信号。作为响应,SRFF 1218进入置位状态并声明信号1216。考虑下一条指令的执行时间和振荡器必要的预热时间,PreAbs32寄存器338用来存储振荡器保持断电的最近的时间。如果当前时间小于它的PreAbs32寄存器338中的时间,序列发生器声明KillSysOsc信号。如果当前时间等于它的PreAbs32寄存器338中的时间,序列发生器声明RestartSysOsc信号。当前时间等于LongWait指令的期满时间时,应该稳定系统时钟。
加电序列发生器1226接收来自或门1220的输入信号,该信号向TEP指示是否有任何内部或外部模块需要使用系统时钟。如果声明了该信号,加电序列发生器1226通过声明SysOscOn信号1236来给系统时钟振荡器加电。时钟pad加电寄存器(CPPUR)1228存储时钟pad缓冲器的设置时间,振荡器预热寄存器OWUR 1230存储振荡器的预热时间。当从或门1220到加电序列发生器1226的输入信号被声明时,FSM 1234从零启动10比特计数器1232并声明SysOscOn信号1236,从而给系统时钟振荡器加电。当计数器1232达到了OWUR 1230中规定的时间,ClkBufOn信号1238被声明,来启动时钟pad缓冲器。当计数器1232等于OWUR 1230中规定的时间和CPPUR 1228中规定的时间相加之和时,SysClkGate信号1240被声明,来表明系统时钟振荡器输出有效并且启用与门1242。与门1242禁止系统时钟振荡器输出直到振荡器有充分的时间稳定。在到达了OWUR 1230中规定的振荡器预热时间与CPPUR 1228中存储的时钟pad加电延迟时间相加的时间之后,振荡器稳定。当到达该时间时,SysClkGate信号1240启用与门1242,并且允许来自振荡器的时钟信号从门通过。
如上所述,时钟和电源控制块216接收来自TEP 138外部资源的ReqSysclk信号。该信号表明是否有任何TEP 138外部的模块需要使用系统振荡器,比如DSP内核102和MCU 104。图13A表示时钟信号如何在通信处理器100中产生。电源1300为系统振荡器1301供电。可以如上所述,电源由来自TEP的SysOscOn信号来控制。该信号被用来控制振荡器1301加电或断电。振荡器输出被输入到pad缓冲放大器1303。缓冲放大器1303通过来自TEP的控制信号加电和断电。缓冲放大器1303的时钟信号输出被输入到与门1305。门1305的第二个输入是来自TEP 138的SysClkGate信号,该信号允许在振荡器预热期间禁止振荡器的输出。
来自门1305的时钟信号输出被输入到锁相环(PLL)1307,它将时钟信号增加到适于为DSP内核102计时的频率。在DSP内核空闲的状态下,不需要使用PLL 1307增加时钟信号,并且从门1305输出的时钟信号不提供给PLL 1307。多路复用器1309或者选择来自PLL1307的被增加的时钟信号,或者选择门1305的输出。如图13B所示,从多路复用器1309的输出可以生成许多时钟信号。首先,DCLK时钟作为PLL 1307的输出而生成。DCLK时钟用来为DSP内核102计时。Not-gated DCLK(nGDCLK)时钟1319输入到与门1311。当DSP内核不需要DCLK时钟时,利用与门1311将其禁止(gate off)。然后,利用分频器1321分割DCLK时钟而生成DSCLK时钟。分频器1321是软件可编程的,用1或2来除DCLK时钟。DSCLK时钟用来为DSP子系统计时,包括DSP外围设备和DSP DMA控制器134。当不需要DSCLK时钟时,利用与门1313将其禁止。Not-gated DSCLK(nGDSCLK)时钟1323提供给可编程分时器1325,它利用1至8之间的数字分割输入信号来生成BCLK时钟。BCLK时钟用来驱动通信处理器100的总线。当不需要BCLK时钟时,利用与门1315将其禁止。MCLK时钟与BCLK时钟的频率相同,用来为MCU 104定时。当不需要MCLK时钟时,利用与门1317将其禁止。
图14A和14B表示在不需要时如何禁止图13B中的时钟信号。如图14A所示,PLL 1307增加振荡器输出以生成时钟信号。分时钟器1419与图13B中的分时器1321和1325执行相同的操作。分时器1419的时钟信号输出是ngDCLK信号、nGDSCLK信号、和nGDBCLK信号。每一个时钟信号直接至多路复用器1309a-1309c之一,然后至适当的与门1311-1315。
寄存器1405是MCU休眠时钟需求寄存器(MSCRR)。如图14B所知,MSCRR寄存器1405表明当MCU休眠或处于空闲模式时需要哪些时钟。同样,MCU激活时钟需求寄存器(MACRR)1407存储关于MCU激活时需要哪些时钟的信息。由MCU 104生成的MCU激活信号1427被多路复用器1423用来确定输出MSCRR寄存器1405或是MACRR寄存器1407的内容。当置位MSCRR寄存器1405中的PLL旁路位时,允许当MCU 104休眠时绕过PLL 1307。因为MCU 104在休眠时不需要定时,所以PLL 1307不需要增加振荡器至高频来驱动MCU 104。因此,绕过PLL 1307可以节省电能。此外,在不需要高处理速度的情况下,DSP内核102和MCU 104可以以未经过PLL累加而输入到通信处理器的系统时钟运行。
与MCU 104同样,也提供了两个DSP寄存器:DSP休眠时钟需求寄存器(DSCRR)1401和DSP激活时钟需求寄存器(DACRR)1403。寄存器1401和1403分别表明当DSP内核102休眠和当DSP内核102激活时各需要哪些时钟。由DSP内核102生成的DSP激活信号被多路复用器1421用来确定输出DSCRR寄存器1401或是DACRR寄存器1403的内容。或门1409、1411、和1413结合MCU需求寄存器1405、1407和DSP需求寄存器1401、1403的输出。与门1415、1311、1313、1315、和1317用来启动或禁止与寄存器1401、1403、1405、和1407的内容相应的时钟信号。
除了当不需要某些时钟信号时将其禁止以节电以外,当通信处理器100没有模块需要时钟时,系统时钟振荡器断电从而不生成系统时钟信号。图15表示如何给振荡器断电。DSP内核102和MCU内核104更新寄存器1503,表明处理内核是否需要时钟信号以及是否有任何外围设备需要时钟信号。时钟控制模块1501监视寄存器以确定通信处理器100是否有任何模块需要时钟信号。如果不需要任何时钟信号,时钟控制模块1501向TEP 138发送SysClkReq信号。如上文参照图12的论述,TEP 138决定是否给系统振荡器断电。按照这样,为了省电,当需要时给系统振荡器加电,不需要时断电。
以上阐述了本发明的各种实施例,本领域的技术人员将做各种改进和变更。因此,本发明的范围不限定于所说明的特定实施例。本发明的范围只由权利要求和与它们等价的部分来限定。
Claims (13)
1.一种数字基带处理器,包括:
至少一个主处理器,用于执行第一指令序列中的指令;和
定时及事件处理器,连接至所述主处理器,用于执行第二指令序列中的定时敏感性指令,
所述定时及事件处理器包括:
两个或多个指令序列发生器,用于执行第二指令序列的线程;
存储器,用于保持用于所述两个或多个指令序列发生器的指令和数据;
时基发生器,用于产生定时信号,该定时信号用于使两个或多个指令序列发生器中每一个中的指令开始执行,其中,所述时基发生器包括时钟校准电路,用于根据相对稳定的高频时钟来校准相对不稳定的低频时钟,并生成校准后的低频时钟;和
绝对计数器,用于计数校准后的低频时钟,并生成可编程的所述定时信号;
I/O冲突裁决器,用于解决由所述两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的输出中的冲突,以及响应冲突而产生异常。
2.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于启动数字基带处理器的元件之间的时间精确的DMA传送的装置。
3.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于能够时间精确地启用数字基带处理器中DMA通道的装置。
4.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于产生时间精确的至所述主处理器的中断的装置。
5.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于产生对数字基带处理器其他元件的时间精确的触发的装置。
6.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于产生时间精确的输出信号的装置。
7.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括用于根据高频时钟校准低频时钟,并生成相位补偿信号的装置。
8.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括响应时基发生器的电源控制电路,用于禁止至数字基带处理器中空闲状态的模块的时钟。
9.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述存储器是多端口的,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括存储器访问裁决器,用于控制所述两个或多个指令序列发生器对存储器的访问。
10.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,还包括DMA控制器,用于处理DMA请求,其中所述定时及事件处理器包括DMA接口,用于启动时间精确的DMA传送。
11.如权利要求10所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括DMA请求裁决器,用于解决由所述两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的DMA请求中的冲突。
12.如权利要求1所述的数字基带处理器,其中所述定时及事件处理器还包括总线接口,用于将所述两个或多个指令序列发生器连接至处理总线。
13.一种数字基带处理器,用于与不同无线系统同时操作,包括:
数字信号处理器,用于执行数字信号处理器指令;
微控制器,用于执行微控制器指令;和
定时及事件处理器,由所述数字信号处理器和所述微处理器控制,用于执行定时敏感性指令,
所述定时及事件处理器包括:
多个指令序列发生器,用于执行定时敏感性指令线程;
存储器,用于保持用于所述多个指令序列发生器的指令和数据;
时基发生器,用于产生定时信号,该定时信号用于使多个指令序列发生器中每一个中的指令开始执行,其中,所述时基发生器包括时钟校准电路,用于根据相对稳定的高频时钟来校准相对不稳定的低频时钟,并生成校准后的低频时钟;和
绝对计数器,用于计数校准后的低频时钟,并生成可编程的所述定时信号;
I/O冲突裁决器,用于解决由所述两个或多个指令序列发生器产生的输出中的冲突,以及响应冲突而产生异常。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US31565501P | 2001-08-29 | 2001-08-29 | |
| US60/315,655 | 2001-08-29 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1620645A CN1620645A (zh) | 2005-05-25 |
| CN100517215C true CN100517215C (zh) | 2009-07-22 |
Family
ID=23225453
Family Applications (9)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028169263A Expired - Lifetime CN100570577C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 高速程序跟踪 |
| CNB028169689A Expired - Lifetime CN100471079C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 用于无线系统中的时钟及电源控制的方法和设备 |
| CNB02816928XA Expired - Lifetime CN100399472C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 用于使用快速突发模式以改善处理器性能的方法和装置 |
| CN2009102091339A Expired - Lifetime CN101673238B (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 程序跟踪器以及程序跟踪方法 |
| CNB028169271A Expired - Lifetime CN100361109C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 通用串行端口体系结构和系统 |
| CN02816976XA Expired - Lifetime CN1549961B (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 动态电压控制方法与设备 |
| CNB028169697A Expired - Lifetime CN100451914C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 锁相环迅速加电方法和装置 |
| CNB028169700A Expired - Lifetime CN100517215C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 用于无线系统中定时及事件处理的方法和装置 |
| CNB028167791A Expired - Lifetime CN1299201C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 通过响应高速缓存缺失而切换任务来提高基于高速缓存的嵌入式处理器的处理能力的方法和装置 |
Family Applications Before (7)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028169263A Expired - Lifetime CN100570577C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 高速程序跟踪 |
| CNB028169689A Expired - Lifetime CN100471079C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 用于无线系统中的时钟及电源控制的方法和设备 |
| CNB02816928XA Expired - Lifetime CN100399472C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 用于使用快速突发模式以改善处理器性能的方法和装置 |
| CN2009102091339A Expired - Lifetime CN101673238B (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 程序跟踪器以及程序跟踪方法 |
| CNB028169271A Expired - Lifetime CN100361109C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 通用串行端口体系结构和系统 |
| CN02816976XA Expired - Lifetime CN1549961B (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 动态电压控制方法与设备 |
| CNB028169697A Expired - Lifetime CN100451914C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 锁相环迅速加电方法和装置 |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028167791A Expired - Lifetime CN1299201C (zh) | 2001-08-29 | 2002-08-29 | 通过响应高速缓存缺失而切换任务来提高基于高速缓存的嵌入式处理器的处理能力的方法和装置 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (10) | US7159134B2 (zh) |
| EP (9) | EP1421588B1 (zh) |
| JP (10) | JP2005502114A (zh) |
| CN (9) | CN100570577C (zh) |
| AU (2) | AU2002331774A1 (zh) |
| DE (6) | DE60211921T2 (zh) |
| WO (8) | WO2003021409A2 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (328)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1421588B1 (en) * | 2001-08-29 | 2012-01-18 | MediaTek Inc. | Method and apparatus utilizing flash burst mode to improve processor performance |
| GB0123421D0 (en) * | 2001-09-28 | 2001-11-21 | Memquest Ltd | Power management system |
| US7502817B2 (en) * | 2001-10-26 | 2009-03-10 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method and apparatus for partitioning memory in a telecommunication device |
| US6944780B1 (en) * | 2002-01-19 | 2005-09-13 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Adaptive voltage scaling clock generator for use in a digital processing component and method of operating the same |
| EP1351117A1 (en) * | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-08 | Hewlett-Packard Company | Data processing system and method |
| US7180322B1 (en) | 2002-04-16 | 2007-02-20 | Transmeta Corporation | Closed loop feedback control of integrated circuits |
| US7941675B2 (en) * | 2002-12-31 | 2011-05-10 | Burr James B | Adaptive power control |
| US7133972B2 (en) | 2002-06-07 | 2006-11-07 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub with internal cache and/or memory access prediction |
| US7117316B2 (en) | 2002-08-05 | 2006-10-03 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub and access method having internal row caching |
| US7149874B2 (en) * | 2002-08-16 | 2006-12-12 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub bypass circuit and method |
| US7836252B2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2010-11-16 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for optimizing interconnections of memory devices in a multichip module |
| US7395447B2 (en) * | 2002-09-16 | 2008-07-01 | Silicon Labs Cp, Inc. | Precision oscillator for an asynchronous transmission system |
| US7774627B2 (en) * | 2002-10-03 | 2010-08-10 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Microprocessor capable of dynamically increasing its performance in response to varying operating temperature |
| US7698583B2 (en) * | 2002-10-03 | 2010-04-13 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Microprocessor capable of dynamically reducing its power consumption in response to varying operating temperature |
| US7290156B2 (en) * | 2003-12-17 | 2007-10-30 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Frequency-voltage mechanism for microprocessor power management |
| US7770042B2 (en) * | 2002-10-03 | 2010-08-03 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Microprocessor with improved performance during P-state transitions |
| US7814350B2 (en) * | 2002-10-03 | 2010-10-12 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Microprocessor with improved thermal monitoring and protection mechanism |
| US7882369B1 (en) | 2002-11-14 | 2011-02-01 | Nvidia Corporation | Processor performance adjustment system and method |
| US7886164B1 (en) | 2002-11-14 | 2011-02-08 | Nvidia Corporation | Processor temperature adjustment system and method |
| US7849332B1 (en) * | 2002-11-14 | 2010-12-07 | Nvidia Corporation | Processor voltage adjustment system and method |
| US7080268B2 (en) * | 2002-12-03 | 2006-07-18 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for regulating power to electronic circuits |
| US7065663B2 (en) * | 2002-12-19 | 2006-06-20 | Intel Corporation | Methods and apparatus to control power state transitions |
| US7146822B2 (en) | 2002-12-30 | 2006-12-12 | Intel Corporation | Centrifugal liquid pump with perimeter magnetic drive |
| US7444524B2 (en) | 2002-12-30 | 2008-10-28 | Intel Corporation | Dynamic voltage transitions |
| US7228242B2 (en) | 2002-12-31 | 2007-06-05 | Transmeta Corporation | Adaptive power control based on pre package characterization of integrated circuits |
| US7811231B2 (en) | 2002-12-31 | 2010-10-12 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Continuous glucose monitoring system and methods of use |
| US8771183B2 (en) | 2004-02-17 | 2014-07-08 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and system for providing data communication in continuous glucose monitoring and management system |
| US7953990B2 (en) * | 2002-12-31 | 2011-05-31 | Stewart Thomas E | Adaptive power control based on post package characterization of integrated circuits |
| CN1759368A (zh) * | 2003-01-23 | 2006-04-12 | 罗切斯特大学 | 多时钟域微处理器 |
| US7206959B1 (en) * | 2003-01-24 | 2007-04-17 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Closed-loop, supply-adjusted ROM memory circuit |
| US7069461B1 (en) * | 2003-01-24 | 2006-06-27 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Closed-loop, supply-adjusted RAM memory circuit |
| US7587287B2 (en) | 2003-04-04 | 2009-09-08 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and system for transferring analyte test data |
| EP1467582B1 (en) * | 2003-04-11 | 2008-03-05 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) | Method for synchronization in a mobile radio terminal |
| CN100416573C (zh) * | 2003-05-07 | 2008-09-03 | 睦塞德技术公司 | 利用电源岛管理集成电路上的功率 |
| JP4033066B2 (ja) | 2003-05-07 | 2008-01-16 | ソニー株式会社 | 周波数制御装置、情報処理装置、周波数制御方法及びプログラム |
| JP2004348662A (ja) * | 2003-05-26 | 2004-12-09 | Toshiba Corp | 電子機器、電源制御装置および電源制御方法 |
| US7375553B1 (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2008-05-20 | Actel Corporation | Clock tree network in a field programmable gate array |
| US8066639B2 (en) | 2003-06-10 | 2011-11-29 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Glucose measuring device for use in personal area network |
| US7245145B2 (en) | 2003-06-11 | 2007-07-17 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory module and method having improved signal routing topology |
| US6822481B1 (en) * | 2003-06-12 | 2004-11-23 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Method and apparatus for clock gating clock trees to reduce power dissipation |
| US7120727B2 (en) | 2003-06-19 | 2006-10-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Reconfigurable memory module and method |
| US7260685B2 (en) | 2003-06-20 | 2007-08-21 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub and access method having internal prefetch buffers |
| US7836222B2 (en) * | 2003-06-26 | 2010-11-16 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method for tracking messages between a processing unit and an external device |
| KR100540483B1 (ko) * | 2003-06-30 | 2006-01-11 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 데이터 억세스 위치에 관계없이 연속적인 버스트 모드로 데이터를 억세스할 수 있는 반도체 메모리 장치 및 그의 구동방법 |
| US7389364B2 (en) | 2003-07-22 | 2008-06-17 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatus and method for direct memory access in a hub-based memory system |
| US7210059B2 (en) * | 2003-08-19 | 2007-04-24 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for on-board diagnostics of memory modules |
| US7133991B2 (en) * | 2003-08-20 | 2006-11-07 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method and system for capturing and bypassing memory transactions in a hub-based memory system |
| US7196562B1 (en) * | 2003-08-26 | 2007-03-27 | Integrated Device Technology, Inc. | Programmable clock drivers that support CRC error checking of configuration data during program restore operations |
| US7136958B2 (en) | 2003-08-28 | 2006-11-14 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Multiple processor system and method including multiple memory hub modules |
| US7287245B2 (en) * | 2003-09-17 | 2007-10-23 | Faraday Technology Corp. | Method for real-time instruction information tracing |
| US7194593B2 (en) | 2003-09-18 | 2007-03-20 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub with integrated non-volatile memory |
| US7225303B2 (en) * | 2003-09-22 | 2007-05-29 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method and apparatus for accessing a dynamic memory device by providing at least one of burst and latency information over at least one of redundant row and column address lines |
| JP4837247B2 (ja) * | 2003-09-24 | 2011-12-14 | パナソニック株式会社 | プロセッサ |
| US7085943B2 (en) * | 2003-09-26 | 2006-08-01 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Method and circuitry for controlling supply voltage in a data processing system |
| US20050081075A1 (en) * | 2003-10-14 | 2005-04-14 | Andrej Kocev | Computer system, carrier medium and method for adjusting an expiration period |
| US7120743B2 (en) | 2003-10-20 | 2006-10-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Arbitration system and method for memory responses in a hub-based memory system |
| TWI254882B (en) * | 2003-11-07 | 2006-05-11 | Via Tech Inc | Rate multiplication method and rate multiplier |
| GB2408357A (en) * | 2003-11-18 | 2005-05-25 | Motorola Inc | Regulating a voltage supply to a semiconductor device |
| US7631307B2 (en) | 2003-12-05 | 2009-12-08 | Intel Corporation | User-programmable low-overhead multithreading |
| US7692477B1 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2010-04-06 | Tien-Min Chen | Precise control component for a substrate potential regulation circuit |
| US7129771B1 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2006-10-31 | Transmeta Corporation | Servo loop for well bias voltage source |
| US7649402B1 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2010-01-19 | Tien-Min Chen | Feedback-controlled body-bias voltage source |
| US7012461B1 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2006-03-14 | Transmeta Corporation | Stabilization component for a substrate potential regulation circuit |
| KR101136036B1 (ko) * | 2003-12-24 | 2012-04-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 유휴 모드에서의 전력 소모가 감소된 프로세서 시스템 및그 방법 |
| US7330992B2 (en) | 2003-12-29 | 2008-02-12 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for read synchronization of memory modules |
| US7188219B2 (en) | 2004-01-30 | 2007-03-06 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Buffer control system and method for a memory system having outstanding read and write request buffers |
| US7788451B2 (en) | 2004-02-05 | 2010-08-31 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatus and method for data bypass for a bi-directional data bus in a hub-based memory sub-system |
| US7412574B2 (en) * | 2004-02-05 | 2008-08-12 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for arbitration of memory responses in a hub-based memory system |
| CN100361040C (zh) * | 2004-02-24 | 2008-01-09 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | 一种soc架构下的处理器核动态变频装置和方法 |
| US7479753B1 (en) | 2004-02-24 | 2009-01-20 | Nvidia Corporation | Fan speed controller |
| US7240170B2 (en) * | 2004-02-25 | 2007-07-03 | Analog Devices, Inc. | High/low priority memory |
| US7366864B2 (en) | 2004-03-08 | 2008-04-29 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub architecture having programmable lane widths |
| US7313707B2 (en) * | 2004-03-09 | 2007-12-25 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Systems and methods for configuring ports |
| US7613911B2 (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2009-11-03 | Arm Limited | Prefetching exception vectors by early lookup exception vectors within a cache memory |
| FI20040418A (fi) * | 2004-03-18 | 2005-09-19 | Nokia Corp | Digitaalijärjestelmän kellokontrolli |
| US7769950B2 (en) * | 2004-03-24 | 2010-08-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Cached memory system and cache controller for embedded digital signal processor |
| US7257683B2 (en) | 2004-03-24 | 2007-08-14 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory arbitration system and method having an arbitration packet protocol |
| US7120723B2 (en) | 2004-03-25 | 2006-10-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for memory hub-based expansion bus |
| US6980042B2 (en) | 2004-04-05 | 2005-12-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Delay line synchronizer apparatus and method |
| US7590797B2 (en) | 2004-04-08 | 2009-09-15 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for optimizing interconnections of components in a multichip memory module |
| US7363419B2 (en) | 2004-05-28 | 2008-04-22 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method and system for terminating write commands in a hub-based memory system |
| US7310748B2 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2007-12-18 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory hub tester interface and method for use thereof |
| US7519788B2 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2009-04-14 | Micron Technology, Inc. | System and method for an asynchronous data buffer having buffer write and read pointers |
| US7971191B2 (en) * | 2004-06-10 | 2011-06-28 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | System and method for analyzing a process |
| US7042260B2 (en) * | 2004-06-14 | 2006-05-09 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Low power and low timing jitter phase-lock loop and method |
| CN101006397A (zh) * | 2004-06-15 | 2007-07-25 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | 用于性能参数的二进制控制的控制方案 |
| EP1607835A1 (en) * | 2004-06-15 | 2005-12-21 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Closed-loop control for performance tuning |
| US7562233B1 (en) | 2004-06-22 | 2009-07-14 | Transmeta Corporation | Adaptive control of operating and body bias voltages |
| US7401241B2 (en) * | 2004-06-22 | 2008-07-15 | Intel Corporation | Controlling standby power of low power devices |
| US7774625B1 (en) * | 2004-06-22 | 2010-08-10 | Eric Chien-Li Sheng | Adaptive voltage control by accessing information stored within and specific to a microprocessor |
| KR100598011B1 (ko) * | 2004-06-29 | 2006-07-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 클럭 사용 회로 및 클럭 신호 발생 방법 |
| US20050008095A1 (en) * | 2004-07-23 | 2005-01-13 | Rush Frederick A. | Apparatus using interrupts for controlling a processor for radio isolation and associated methods |
| US8472990B2 (en) * | 2004-07-23 | 2013-06-25 | St Ericsson Sa | Apparatus using interrupts for controlling a processor for radio isolation and associated method |
| US7312487B2 (en) * | 2004-08-16 | 2007-12-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Three dimensional integrated circuit |
| US7681065B2 (en) * | 2004-08-16 | 2010-03-16 | Broadcom Corporation | Method and system for a message processor switch for performing incremental redundancy in edge compliant terminals |
| US7308590B2 (en) | 2004-10-15 | 2007-12-11 | Intel Corporation | Automatic dynamic processor operating voltage control |
| US7434073B2 (en) * | 2004-11-29 | 2008-10-07 | Intel Corporation | Frequency and voltage scaling architecture |
| US7456829B2 (en) * | 2004-12-03 | 2008-11-25 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Methods and systems to control electronic display brightness |
| CN1319274C (zh) * | 2004-12-10 | 2007-05-30 | 展讯通信(上海)有限公司 | 射频接收系统锁定时间及锁定后频率误差的评估方法 |
| US7379718B2 (en) | 2004-12-20 | 2008-05-27 | Marvell World Trade Ltd. | Method and apparatus to manage power consumption of a semiconductor device |
| US7337335B2 (en) * | 2004-12-21 | 2008-02-26 | Packet Digital | Method and apparatus for on-demand power management |
| US7228446B2 (en) * | 2004-12-21 | 2007-06-05 | Packet Digital | Method and apparatus for on-demand power management |
| FR2882449A1 (fr) * | 2005-01-21 | 2006-08-25 | Meiosys Soc Par Actions Simpli | Procede non intrusif de rejeu d'evenements internes au sein d'un processus applicatif, et systeme mettant en oeuvre ce procede |
| FR2881246B1 (fr) * | 2005-01-21 | 2007-03-23 | Meiosys Soc Par Actions Simpli | Procede perdictif de gestion, de journalisation ou de rejeu d'operations non deterministes au sein du deroulement d'un processus applicatif |
| US7409520B2 (en) * | 2005-01-25 | 2008-08-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Systems and methods for time division multiplex multithreading |
| JP2006236241A (ja) * | 2005-02-28 | 2006-09-07 | Toshiba Corp | 周辺装置 |
| US20060215567A1 (en) * | 2005-03-25 | 2006-09-28 | Arun Raghunath | Method and apparatus for monitoring path statistics |
| US7529911B1 (en) * | 2005-05-26 | 2009-05-05 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Hardware-based technique for improving the effectiveness of prefetching during scout mode |
| CN1881798B (zh) * | 2005-06-16 | 2011-08-31 | 旺玖科技股份有限公司 | 有理数倍频电路与产生有理数倍频的方法 |
| US8745627B2 (en) * | 2005-06-27 | 2014-06-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | System and method of controlling power in a multi-threaded processor |
| US20070008011A1 (en) * | 2005-06-29 | 2007-01-11 | Paulette Thurston | Distributed power and clock management in a computerized system |
| CN101223490A (zh) * | 2005-07-14 | 2008-07-16 | Nxp股份有限公司 | 使用历史负载简档来动态调整手持多媒体设备处理器内核的工作频率及可用功率 |
| US7953960B2 (en) * | 2005-10-18 | 2011-05-31 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for delaying a load miss flush until issuing the dependent instruction |
| CN101297255B (zh) * | 2005-10-26 | 2011-11-02 | 英特尔公司 | 可检测变化的集群体系结构 |
| US7766829B2 (en) * | 2005-11-04 | 2010-08-03 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and system for providing basal profile modification in analyte monitoring and management systems |
| US8253748B1 (en) | 2005-11-29 | 2012-08-28 | Nvidia Corporation | Shader performance registers |
| US7809928B1 (en) * | 2005-11-29 | 2010-10-05 | Nvidia Corporation | Generating event signals for performance register control using non-operative instructions |
| TW200805047A (en) * | 2005-12-23 | 2008-01-16 | Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | Performance analysis based system level power management |
| CN100346306C (zh) * | 2006-01-06 | 2007-10-31 | 浙江大学 | 基于动态调频技术的节能编译方法 |
| US7499724B2 (en) * | 2006-01-30 | 2009-03-03 | Harris Corporation | Event sequencer used for controlling the sequence and timing of events in software defined radio |
| JP2007233718A (ja) * | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-13 | Canon Inc | 制御装置及び半導体集積回路 |
| US20070214374A1 (en) * | 2006-03-13 | 2007-09-13 | Mark Hempstead | Ultra low power system for sensor network applications |
| US8226891B2 (en) | 2006-03-31 | 2012-07-24 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring devices and methods therefor |
| US7620438B2 (en) | 2006-03-31 | 2009-11-17 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and system for powering an electronic device |
| US7617409B2 (en) * | 2006-05-01 | 2009-11-10 | Arm Limited | System for checking clock-signal correspondence |
| US7502913B2 (en) | 2006-06-16 | 2009-03-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Switch prefetch in a multicore computer chip |
| DE502006006706D1 (de) * | 2006-06-20 | 2010-05-27 | Siemens Ag | Verfahren zur Überwachung eines zyklischen Steuerungsprogramms |
| US7814339B2 (en) * | 2006-06-30 | 2010-10-12 | Intel Corporation | Leakage power estimation |
| US7672393B2 (en) * | 2006-08-02 | 2010-03-02 | Richtek Technology Corporation | Single-wire asynchronous serial interface |
| EP1895426A1 (en) * | 2006-08-25 | 2008-03-05 | Ali Corporation | Transmitter and transmitting system utilizing the same |
| JP4808108B2 (ja) | 2006-08-29 | 2011-11-02 | パナソニック株式会社 | プロセッサシステム |
| US8200807B2 (en) * | 2006-08-31 | 2012-06-12 | The Mathworks, Inc. | Non-blocking local events in a state-diagramming environment |
| US7958291B2 (en) * | 2006-10-10 | 2011-06-07 | Atmel Rousset S.A.S. | Supplemental communication interface |
| US7840825B2 (en) * | 2006-10-24 | 2010-11-23 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for autonomous dynamic voltage and frequency scaling of microprocessors |
| EP1919103B8 (en) * | 2006-11-02 | 2016-11-30 | Google Technology Holdings LLC | Method and apparatus for automatic frequency correction in a multimode device |
| WO2008056293A2 (en) * | 2006-11-08 | 2008-05-15 | Nxp B.V. | Fast adaptive voltage scaling |
| TWI335531B (en) * | 2006-12-13 | 2011-01-01 | Inst Information Industry | Apparatus, method, application program, and computer readable medium thereof for generating and utilizing a feature code to monitor a program |
| US7840849B2 (en) * | 2006-12-21 | 2010-11-23 | Novell, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for debugging software including divisions of an execution history of a debuggee program |
| US7917784B2 (en) * | 2007-01-07 | 2011-03-29 | Apple Inc. | Methods and systems for power management in a data processing system |
| US8667198B2 (en) * | 2007-01-07 | 2014-03-04 | Apple Inc. | Methods and systems for time keeping in a data processing system |
| US7949801B2 (en) * | 2007-01-31 | 2011-05-24 | Pitney Bowes Inc. | Main processor initiating command timing signal via DMA to coprocessor in order to synchronize execution of instructions |
| US20080199894A1 (en) | 2007-02-15 | 2008-08-21 | Abbott Diabetes Care, Inc. | Device and method for automatic data acquisition and/or detection |
| US8123686B2 (en) | 2007-03-01 | 2012-02-28 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and apparatus for providing rolling data in communication systems |
| US7937076B2 (en) * | 2007-03-07 | 2011-05-03 | Harris Corporation | Software defined radio for loading waveform components at runtime in a software communications architecture (SCA) framework |
| JP4950716B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-22 | 2012-06-13 | 株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ | 画像処理システム、及び走査型電子顕微鏡装置 |
| US7900069B2 (en) * | 2007-03-29 | 2011-03-01 | Intel Corporation | Dynamic power reduction |
| US7743279B2 (en) | 2007-04-06 | 2010-06-22 | Apple Inc. | Program counter (PC) trace |
| US7917799B2 (en) * | 2007-04-12 | 2011-03-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and system for digital frequency clocking in processor cores |
| US8161314B2 (en) * | 2007-04-12 | 2012-04-17 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and system for analog frequency clocking in processor cores |
| DE102007019543A1 (de) | 2007-04-25 | 2008-10-30 | Rohde & Schwarz Gmbh & Co. Kg | Messgerät mit serieller digitaler Schnittstelle |
| US9134782B2 (en) | 2007-05-07 | 2015-09-15 | Nvidia Corporation | Maintaining optimum voltage supply to match performance of an integrated circuit |
| US8456301B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2013-06-04 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring system and methods |
| US7928850B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2011-04-19 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring system and methods |
| US8461985B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2013-06-11 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring system and methods |
| US8665091B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2014-03-04 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Method and device for determining elapsed sensor life |
| US20080281171A1 (en) * | 2007-05-08 | 2008-11-13 | Abbott Diabetes Care, Inc. | Analyte monitoring system and methods |
| US7845568B2 (en) * | 2007-05-09 | 2010-12-07 | Atmel Rousset S.A.S. | Managing power and timing in a smart card device |
| JP5209046B2 (ja) * | 2007-05-23 | 2013-06-12 | アギア システムズ インコーポレーテッド | 単一及び複数の無線技術通信システムにおいて移動体デバイスの時間節約型セル検索のためのシステム及び方法 |
| US8645740B2 (en) * | 2007-06-08 | 2014-02-04 | Apple Inc. | Methods and systems to dynamically manage performance states in a data processing system |
| US9313067B2 (en) * | 2007-08-14 | 2016-04-12 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Multi-bandwidth communication system using a shared baseband processor |
| US7711864B2 (en) | 2007-08-31 | 2010-05-04 | Apple Inc. | Methods and systems to dynamically manage performance states in a data processing system |
| US7921312B1 (en) | 2007-09-14 | 2011-04-05 | National Semiconductor Corporation | System and method for providing adaptive voltage scaling with multiple clock domains inside a single voltage domain |
| TWI402647B (zh) * | 2007-09-14 | 2013-07-21 | Asustek Comp Inc | 可動態調整電壓及有效節能之電壓控制裝置、方法及電腦裝置 |
| GB2453174B (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2011-12-07 | Advanced Risc Mach Ltd | Techniques for generating a trace stream for a data processing apparatus |
| US7945804B2 (en) * | 2007-10-17 | 2011-05-17 | International Business Machines Corporation | Methods and systems for digitally controlled multi-frequency clocking of multi-core processors |
| US9354890B1 (en) | 2007-10-23 | 2016-05-31 | Marvell International Ltd. | Call stack structure for enabling execution of code outside of a subroutine and between call stack frames |
| US20090108817A1 (en) * | 2007-10-30 | 2009-04-30 | Topower Computer Industrial Co., Ltd. | Method for actuation by boosting power source voltage |
| CN101436167B (zh) * | 2007-11-16 | 2011-03-23 | 宏达国际电子股份有限公司 | 解译串行传输信号的方法 |
| US8578193B2 (en) * | 2007-11-28 | 2013-11-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus, method and program product for adaptive real-time power and perfomance optimization of multi-core processors |
| KR20090059602A (ko) * | 2007-12-07 | 2009-06-11 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 세션 메모리 버스를 구비한 암호화 장치 |
| GB0724337D0 (en) * | 2007-12-13 | 2008-01-23 | Icera Inc | Radio access technology |
| US8589706B2 (en) | 2007-12-26 | 2013-11-19 | Intel Corporation | Data inversion based approaches for reducing memory power consumption |
| US20090182802A1 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2009-07-16 | Microsoft Corporation | Mobile device management scheduling |
| US8166145B2 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2012-04-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Managing event-based conditional recurrent schedules |
| US8230436B2 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2012-07-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Aggregating recurrent schedules to optimize resource consumption |
| US7841436B2 (en) | 2008-01-21 | 2010-11-30 | Amigo Mobility International | Personal mobility vehicle |
| US8370663B2 (en) | 2008-02-11 | 2013-02-05 | Nvidia Corporation | Power management with dynamic frequency adjustments |
| US8595538B2 (en) * | 2008-03-03 | 2013-11-26 | Quintic Holdings | Single-clock-based multiple-clock frequency generator |
| US8312299B2 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2012-11-13 | Packet Digital | Method and apparatus for dynamic power management control using serial bus management protocols |
| EP2472727B1 (en) * | 2008-03-31 | 2013-07-24 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (publ) | Digital baseband circuit |
| US7826382B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2010-11-02 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Close proximity communication device and methods |
| US8112475B2 (en) * | 2008-06-27 | 2012-02-07 | Microsoft Corporation | Managing data delivery based on device state |
| US8090826B2 (en) * | 2008-06-27 | 2012-01-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Scheduling data delivery to manage device resources |
| US8904083B2 (en) * | 2008-07-30 | 2014-12-02 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Method and apparatus for storing data in solid state memory |
| JP2010072897A (ja) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-04-02 | Nec Electronics Corp | クロック供給装置 |
| US8122270B2 (en) * | 2008-09-29 | 2012-02-21 | Intel Corporation | Voltage stabilization for clock signal frequency locking |
| US8127160B2 (en) | 2008-10-13 | 2012-02-28 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dynamic frequency and voltage scaling for a computer processor |
| JP2010097277A (ja) * | 2008-10-14 | 2010-04-30 | Toshiba Corp | 情報処理装置 |
| US20100094572A1 (en) * | 2008-10-15 | 2010-04-15 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dynamic Frequency And Voltage Scaling For A Computer Processor |
| JP5509579B2 (ja) * | 2008-11-21 | 2014-06-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 映像出力装置および映像出力方法ならびにプロジェクタ |
| JP5330409B2 (ja) | 2008-11-28 | 2013-10-30 | パナソニック株式会社 | メモリ制御装置、データプロセッサ及びデータ読み出し方法 |
| TWI363498B (en) * | 2008-12-03 | 2012-05-01 | Ind Tech Res Inst | A tri-mode delay type phase lock loop |
| JP5816407B2 (ja) * | 2009-02-27 | 2015-11-18 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体集積回路装置 |
| US8285917B2 (en) * | 2009-03-26 | 2012-10-09 | Scaleo Chip | Apparatus for enhancing flash memory access |
| US9226701B2 (en) | 2009-04-28 | 2016-01-05 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Error detection in critical repeating data in a wireless sensor system |
| EP2424426B1 (en) * | 2009-04-29 | 2020-01-08 | Abbott Diabetes Care, Inc. | Method and system for providing data communication in continuous glucose monitoring and management system |
| US9184490B2 (en) | 2009-05-29 | 2015-11-10 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Medical device antenna systems having external antenna configurations |
| US9314195B2 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2016-04-19 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte signal processing device and methods |
| WO2011026148A1 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2011-03-03 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring system and methods for managing power and noise |
| EP2290542B1 (en) * | 2009-09-01 | 2013-03-27 | Research In Motion Limited | System and method for sequencing radio items for a multi downlink multi carrier receiver |
| US8213974B2 (en) * | 2009-09-01 | 2012-07-03 | Research In Motion Limited | System and method for sequencing radio items for a multi downlink multi carrier receiver |
| JP2011118469A (ja) | 2009-11-30 | 2011-06-16 | Toshiba Corp | メモリ管理装置およびメモリ管理方法 |
| JP2011139370A (ja) * | 2009-12-28 | 2011-07-14 | Canon Inc | 電子機器とその制御方法 |
| US9256265B2 (en) | 2009-12-30 | 2016-02-09 | Nvidia Corporation | Method and system for artificially and dynamically limiting the framerate of a graphics processing unit |
| US9830889B2 (en) | 2009-12-31 | 2017-11-28 | Nvidia Corporation | Methods and system for artifically and dynamically limiting the display resolution of an application |
| US9582443B1 (en) * | 2010-02-12 | 2017-02-28 | Marvell International Ltd. | Serial control channel processor for executing time-based instructions |
| US9000804B2 (en) | 2010-03-03 | 2015-04-07 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Integrated circuit device comprising clock gating circuitry, electronic device and method for dynamically configuring clock gating |
| US8423802B2 (en) * | 2010-04-07 | 2013-04-16 | Andes Technology Corporation | Power scaling module and power scaling unit of an electronic system having a function unit in a standby state which is insensitive to change in frequency or voltage during synchronization |
| US8839006B2 (en) | 2010-05-28 | 2014-09-16 | Nvidia Corporation | Power consumption reduction systems and methods |
| US8766666B2 (en) | 2010-06-10 | 2014-07-01 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Programmable device, hierarchical parallel machines, and methods for providing state information |
| CN101860353B (zh) * | 2010-06-17 | 2012-02-29 | 广州市广晟微电子有限公司 | 数模混合芯片中的时钟电路控制装置及方法 |
| US8667308B2 (en) | 2010-06-18 | 2014-03-04 | Apple Inc. | Dynamic voltage dithering |
| WO2012004863A1 (ja) * | 2010-07-07 | 2012-01-12 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | データ処理装置およびデータ処理システム |
| US20120017035A1 (en) * | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Plx Technology, Inc. | Runtime reprogramming of a processor code space memory area |
| US9996102B2 (en) | 2010-07-20 | 2018-06-12 | Nxp Usa, Inc. | Clock circuit and method for providing an electronic device with an adjustable clock signal |
| JP2012033001A (ja) | 2010-07-30 | 2012-02-16 | Toshiba Corp | 情報処理装置および情報処理方法 |
| US20120042212A1 (en) * | 2010-08-10 | 2012-02-16 | Gilbert Laurenti | Mixed Mode Processor Tracing |
| JP5598161B2 (ja) * | 2010-08-26 | 2014-10-01 | ヤマハ株式会社 | クロック発生回路 |
| US8732495B2 (en) | 2010-08-31 | 2014-05-20 | Integrated Device Technology, Inc. | Systems, apparatuses and methods for dynamic voltage and frequency control of components used in a computer system |
| WO2012030329A1 (en) * | 2010-08-31 | 2012-03-08 | Integrated Device Technology, Inc. | Systems, apparatuses and methods for dynamic voltage and frequency control of components used in a computer system |
| US20120072632A1 (en) * | 2010-09-17 | 2012-03-22 | Paul Kimelman | Deterministic and non-Deterministic Execution in One Processor |
| JP5581960B2 (ja) * | 2010-10-14 | 2014-09-03 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN102457270B (zh) * | 2010-10-29 | 2013-09-04 | 扬智科技股份有限公司 | 低增益压控振荡器的控制方法 |
| GB2499151B (en) * | 2010-11-09 | 2016-04-20 | Ibm | Energy capture of time-varying energy sources by varying computation workload |
| CN103404031B (zh) * | 2010-12-01 | 2016-01-20 | 爱立信(中国)通信有限公司 | 锁相环控制电压确定 |
| DE102011122074A1 (de) | 2010-12-20 | 2012-06-21 | Dmos Gmbh | Bussystem zur Kommunikation und Stromversorgung von Teilnehmerschaltungen und Verfahren zur Reduzierung des Energieverbrauchs in Baugruppen von Bussystemen |
| CN102082506B (zh) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-12-12 | 复旦大学 | 适用于开关电源转换器的时钟频率选择电路 |
| CN102611148A (zh) * | 2011-01-24 | 2012-07-25 | 祥硕科技股份有限公司 | 配置充电端口的方法与控制器 |
| TW201232239A (en) * | 2011-01-24 | 2012-08-01 | Asmedia Technology Inc | Method and controller allocating charging ports |
| JP5284401B2 (ja) | 2011-03-24 | 2013-09-11 | 株式会社東芝 | 動作切替装置およびプログラム |
| US8856571B2 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2014-10-07 | Apple Inc. | Adjusting device performance over multiple time domains |
| US8572421B2 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2013-10-29 | Apple Inc. | Adjusting device performance based on processing profiles |
| US9588881B2 (en) | 2011-05-16 | 2017-03-07 | Cypress Semiconductor Corporation | Stack processor using a ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) for code space and a portion of the stack memory space having an instruction set optimized to minimize processor stack accesses |
| US9910823B2 (en) | 2011-05-16 | 2018-03-06 | Cypress Semiconductor Corporation | Stack processor using a ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) having an instruction set optimized to minimize memory fetch |
| US8934279B2 (en) * | 2011-05-16 | 2015-01-13 | Cypress Semiconductor Corporation | Stack processor using a ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) for code space and a portion of the stack memory space |
| US9135082B1 (en) * | 2011-05-20 | 2015-09-15 | Google Inc. | Techniques and systems for data race detection |
| CN102170499B (zh) * | 2011-05-24 | 2013-10-02 | 惠州Tcl移动通信有限公司 | 一种移动终端及其电源控制系统 |
| US8884920B1 (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2014-11-11 | Marvell International Ltd. | Programmatic sensing of capacitive sensors |
| US8855969B2 (en) | 2011-06-27 | 2014-10-07 | International Business Machines Corporation | Frequency guard band validation of processors |
| US9098694B1 (en) | 2011-07-06 | 2015-08-04 | Marvell International Ltd. | Clone-resistant logic |
| US9081517B2 (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2015-07-14 | Apple Inc. | Hardware-based automatic clock gating |
| US9069553B2 (en) | 2011-09-06 | 2015-06-30 | Marvell World Trade Ltd. | Switching tasks between heterogeneous cores |
| GB2495959A (en) * | 2011-10-26 | 2013-05-01 | Imagination Tech Ltd | Multi-threaded memory access processor |
| US9980669B2 (en) | 2011-11-07 | 2018-05-29 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Analyte monitoring device and methods |
| JP2013106166A (ja) * | 2011-11-14 | 2013-05-30 | Sony Corp | クロックゲーティング回路およびバスシステム |
| CN104011693B (zh) * | 2011-12-21 | 2017-09-12 | 英特尔公司 | 设置基于i/o带宽的处理器频率层的装置和方法 |
| CN102594344B (zh) * | 2012-01-09 | 2015-03-18 | 青岛海信移动通信技术股份有限公司 | 一种集中式时钟装置和移动终端设备 |
| TWI497304B (zh) * | 2012-03-13 | 2015-08-21 | Novatek Microelectronics Corp | 序列介面傳送方法及其裝置 |
| CN103324588B (zh) * | 2012-03-22 | 2016-05-04 | 联咏科技股份有限公司 | 序列接口传送方法及其装置 |
| US8943352B1 (en) | 2012-05-07 | 2015-01-27 | Dust Networks, Inc. | Low power timing, configuring, and scheduling |
| JP6103825B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-07 | 2017-03-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | 半導体集積回路、情報処理装置 |
| US9317460B2 (en) * | 2012-06-15 | 2016-04-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Program event recording within a transactional environment |
| CN103513698B (zh) * | 2012-06-29 | 2017-03-01 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | 一种时钟信号校准方法、装置及电子设备 |
| US8710879B2 (en) * | 2012-07-06 | 2014-04-29 | Silicon Integrated System Corp. | Apparatus and method for multiplying frequency of a clock signal |
| US9968306B2 (en) | 2012-09-17 | 2018-05-15 | Abbott Diabetes Care Inc. | Methods and apparatuses for providing adverse condition notification with enhanced wireless communication range in analyte monitoring systems |
| US9129072B2 (en) * | 2012-10-15 | 2015-09-08 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Virtual GPIO |
| US9530398B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2016-12-27 | White Eagle Sonic Technologies, Inc. | Method for adaptively scheduling ultrasound system actions |
| US9983905B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2018-05-29 | White Eagle Sonic Technologies, Inc. | Apparatus and system for real-time execution of ultrasound system actions |
| US10499884B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2019-12-10 | White Eagle Sonic Technologies, Inc. | System and method for scanning for a second object within a first object using an adaptive scheduler |
| US9529080B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2016-12-27 | White Eagle Sonic Technologies, Inc. | System and apparatus having an application programming interface for flexible control of execution ultrasound actions |
| US10076313B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2018-09-18 | White Eagle Sonic Technologies, Inc. | System and method for automatically adjusting beams to scan an object in a body |
| DE102013001143A1 (de) * | 2013-01-23 | 2014-07-24 | Giesecke & Devrient Gmbh | Verfahren zur Ausvührung eines Programms über einen Mikroprozessor auf einem Sicherheitsmodul |
| JP5892083B2 (ja) * | 2013-02-12 | 2016-03-23 | 日本電気株式会社 | パラメータ設定装置、パラメータ設定プログラム及びパラメータ設定方法 |
| US9823719B2 (en) | 2013-05-31 | 2017-11-21 | Intel Corporation | Controlling power delivery to a processor via a bypass |
| US9256276B2 (en) * | 2013-09-27 | 2016-02-09 | Intel Corporation | Utilization of processor capacity at low operating frequencies |
| EP4254209A3 (en) * | 2013-10-30 | 2023-11-22 | INTEL Corporation | A method, apparatus and system for measuring latency in a physical unit of a circuit |
| US9814106B2 (en) * | 2013-10-30 | 2017-11-07 | Apple Inc. | Backlight driver chip incorporating a phase lock loop (PLL) with programmable offset/delay and seamless operation |
| TWI497314B (zh) * | 2013-11-06 | 2015-08-21 | Univ Nat Chiao Tung | 適應性計算之無線處理器 |
| JP6381899B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-05 | 2018-08-29 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置の設計方法、設計支援プログラム、設計装置、及び、半導体装置 |
| US10200951B2 (en) * | 2014-02-20 | 2019-02-05 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Low power low latency protocol for data exchange |
| KR102320399B1 (ko) * | 2014-08-26 | 2021-11-03 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 전원 관리 칩, 그것을 포함하는 모바일 장치 및 그것의 클록 조절 방법 |
| US9841795B2 (en) | 2014-09-22 | 2017-12-12 | Nxp Usa, Inc. | Method for resetting an electronic device having independent device domains |
| KR102271469B1 (ko) | 2014-10-24 | 2021-06-30 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 장치 및 이를 포함하는 반도체 시스템 |
| CN104699578B (zh) * | 2015-01-09 | 2017-12-26 | 同济大学 | 一种以内升温方式检测时延故障的定温指令级自测试方法 |
| US9450582B2 (en) | 2015-02-03 | 2016-09-20 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Programmable buffer system |
| US9696782B2 (en) | 2015-02-09 | 2017-07-04 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Battery parameter-based power management for suppressing power spikes |
| US10158148B2 (en) | 2015-02-18 | 2018-12-18 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Dynamically changing internal state of a battery |
| US9748765B2 (en) | 2015-02-26 | 2017-08-29 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Load allocation for multi-battery devices |
| JP6466740B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-02 | 2019-02-06 | 株式会社メガチップス | クロック生成回路 |
| WO2016164543A1 (en) | 2015-04-07 | 2016-10-13 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Quality factor estimation for resonators |
| US10432337B2 (en) * | 2015-05-15 | 2019-10-01 | Avago Technologies International Sales Pte. Limited | Apparatus and method for timestamping of data packets |
| CN104881529B (zh) * | 2015-05-18 | 2018-05-29 | 南京航空航天大学 | 基于有限状态机的采样保持控制策略的实现方法 |
| US10210919B2 (en) | 2015-06-03 | 2019-02-19 | Altera Corporation | Integrated circuits with embedded double-clocked components |
| US9503067B1 (en) * | 2015-06-22 | 2016-11-22 | Realtek Semiconductor Corporation | Time shifter and method thereof |
| US9874863B2 (en) * | 2015-08-24 | 2018-01-23 | Keysight Technologies, Inc. | Finite state machine-based trigger event detection employing interpolation |
| US9939862B2 (en) | 2015-11-13 | 2018-04-10 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Latency-based energy storage device selection |
| US10061366B2 (en) | 2015-11-17 | 2018-08-28 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Schedule-based energy storage device selection |
| US9793570B2 (en) | 2015-12-04 | 2017-10-17 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Shared electrode battery |
| CN105608027B (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2018-10-19 | 华为技术有限公司 | 非易失存储设备和访问非易失存储设备的方法 |
| US10303203B2 (en) | 2016-01-25 | 2019-05-28 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device, semiconductor system and method for operating semiconductor device |
| DE102017110821A1 (de) | 2016-01-25 | 2018-07-26 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Halbleitervorrichtung |
| US10248155B2 (en) | 2016-01-25 | 2019-04-02 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device including clock generating circuit and channel management circuit |
| US10296066B2 (en) | 2016-01-25 | 2019-05-21 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device, semiconductor system, and method of operating the semiconductor device |
| US10209734B2 (en) | 2016-01-25 | 2019-02-19 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device, semiconductor system, and method of operating the semiconductor device |
| KR102467172B1 (ko) * | 2016-01-25 | 2022-11-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 장치 |
| KR102474620B1 (ko) * | 2016-01-25 | 2022-12-05 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 장치, 반도체 시스템 및 반도체 장치의 동작 방법 |
| JP2017191564A (ja) * | 2016-04-15 | 2017-10-19 | 富士通株式会社 | 演算処理装置及び演算処理装置の制御方法 |
| US10445099B2 (en) * | 2016-04-19 | 2019-10-15 | Xiaolin Wang | Reconfigurable microprocessor hardware architecture |
| KR20170124017A (ko) * | 2016-04-29 | 2017-11-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 동작 전압을 조절하는 메모리 장치, 메모리 장치를 제어하는 어플리케이션 프로세서 및 메모리 장치의 동작방법 |
| JP6594533B2 (ja) * | 2016-05-17 | 2019-10-23 | 三菱電機株式会社 | コントローラシステム |
| US10254782B2 (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2019-04-09 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses for reducing clock path power consumption in low power dynamic random access memory |
| US10305495B2 (en) * | 2016-10-06 | 2019-05-28 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Phase control of clock signal based on feedback |
| US10659063B2 (en) * | 2016-11-01 | 2020-05-19 | Nvidia Corporation | Adaptive voltage frequency scaling for optimal power efficiency |
| JP2018120449A (ja) * | 2017-01-26 | 2018-08-02 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | 演算処理装置および情報処理システム |
| JP6819327B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-03 | 2021-01-27 | 富士通株式会社 | クロック生成回路、シリアル・パラレル変換回路及び情報処理装置 |
| TW201838392A (zh) * | 2017-02-10 | 2018-10-16 | 香港商凱歐斯科技(香港)有限公司 | 功能型手機及其操作方法 |
| US10120819B2 (en) * | 2017-03-20 | 2018-11-06 | Nxp Usa, Inc. | System and method for cache memory line fill using interrupt indication |
| KR102435034B1 (ko) * | 2017-06-21 | 2022-08-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 디지털 위상 고정 루프 및 디지털 위상 고정 루프의 동작 방법 |
| US10809790B2 (en) * | 2017-06-30 | 2020-10-20 | Intel Corporation | Dynamic voltage-level clock tuning |
| US10578435B2 (en) | 2018-01-12 | 2020-03-03 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Quality factor compensation in microelectromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscopes |
| US11360504B2 (en) * | 2018-05-25 | 2022-06-14 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Adaptable voltage margin for a processor |
| EP3806336A4 (en) | 2018-06-05 | 2021-08-04 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | INPUT / OUTPUT CIRCUIT |
| GB201810478D0 (en) * | 2018-06-26 | 2018-08-08 | Nordic Semiconductor Asa | Precision timing between systems |
| US11041722B2 (en) | 2018-07-23 | 2021-06-22 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Systems and methods for sensing angular motion in the presence of low-frequency noise |
| CN111435267A (zh) * | 2019-01-15 | 2020-07-21 | 海信集团有限公司 | 功耗自动调整的方法、装置、设备及计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN109787625B (zh) * | 2019-03-05 | 2022-04-05 | 上海芷锐电子科技有限公司 | 一种基于双pll的系统超频引起的电压毛刺保护系统 |
| IT201900006633A1 (it) * | 2019-05-08 | 2020-11-08 | Stmicroelectronics Application Gmbh | Sistema di elaborazione, relativo circuito integrato, dispositivo e procedimento |
| CN110081933B (zh) * | 2019-05-10 | 2021-07-20 | 上海岚盒信息技术有限公司 | 振动巡检仪及其低功耗频域变换方法、计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN110413558A (zh) * | 2019-07-15 | 2019-11-05 | 广芯微电子(广州)股份有限公司 | 一种实现低功耗串口模块动态分频方法 |
| KR20210062499A (ko) * | 2019-11-21 | 2021-05-31 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | 반도체 메모리 장치 및 그 동작 방법 |
| CN112104537B (zh) * | 2020-03-28 | 2022-04-19 | 上海芯郡电子科技有限公司 | 一种通信控制器 |
| KR102414817B1 (ko) * | 2020-05-25 | 2022-06-30 | 윈본드 일렉트로닉스 코포레이션 | 지연 락 루프 디바이스와 그 동작 방법 |
| US11455264B2 (en) | 2020-08-10 | 2022-09-27 | International Business Machines Corporation | Minimizing delay while migrating direct memory access (DMA) mapped pages |
| US11656876B2 (en) * | 2020-10-29 | 2023-05-23 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Removal of dependent instructions from an execution pipeline |
| TWI749960B (zh) * | 2020-12-23 | 2021-12-11 | 瑞昱半導體股份有限公司 | 資料處理裝置與其資料存取電路 |
| KR102392119B1 (ko) | 2021-07-21 | 2022-04-27 | 중앙대학교 산학협력단 | 위상 회전자를 이용한 분수 서브 샘플링 위상 고정 루프 |
| US11853237B2 (en) * | 2021-11-19 | 2023-12-26 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Input/output sequencer instruction set processing |
| US20230378962A1 (en) * | 2022-05-20 | 2023-11-23 | Apple Inc. | Clock Frequency Limiter |
Family Cites Families (105)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3680050A (en) * | 1970-07-10 | 1972-07-25 | Gen Electric | Serial digital pulse phase interface driver and receiver |
| US4110708A (en) * | 1977-03-25 | 1978-08-29 | Harris Corporation | Multichannel modulation system including automatic gain shifter |
| GB2031676B (en) * | 1978-09-02 | 1983-05-11 | Marconi Instruments Ltd | Frequency modulation systems |
| CH620087B (de) * | 1979-03-09 | Suisse Horlogerie | Oszillator mit einem hochfrequenz-quarzresonator. | |
| JPS5837737B2 (ja) | 1979-11-05 | 1983-08-18 | 株式会社日立国際電気 | デイジタル符号の伝送方式 |
| JPS61287335A (ja) | 1985-06-13 | 1986-12-17 | Toshiba Corp | パリテイ−生成回路 |
| JPS63126018A (ja) * | 1986-11-17 | 1988-05-30 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体集積回路 |
| US6760866B2 (en) * | 1987-06-02 | 2004-07-06 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Process of operating a processor with domains and clocks |
| US5535331A (en) * | 1987-09-04 | 1996-07-09 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Processor condition sensing circuits, systems and methods |
| JP2668898B2 (ja) * | 1987-11-06 | 1997-10-27 | 富士通株式会社 | バス制御回路 |
| EP0479887A4 (en) * | 1989-06-30 | 1992-08-12 | Poqet Computer Corporation | Computer power management system |
| GB2237157A (en) | 1989-10-20 | 1991-04-24 | Marconi Instruments Ltd | Control of frequency modulators |
| US5038117A (en) * | 1990-01-23 | 1991-08-06 | Hewlett-Packard Company | Multiple-modulator fractional-N divider |
| US6693951B1 (en) * | 1990-06-25 | 2004-02-17 | Qualcomm Incorporated | System and method for generating signal waveforms in a CDMA cellular telephone system |
| US5159205A (en) * | 1990-10-24 | 1992-10-27 | Burr-Brown Corporation | Timing generator circuit including adjustable tapped delay line within phase lock loop to control timing of signals in the tapped delay line |
| JPH05119876A (ja) * | 1991-10-25 | 1993-05-18 | Toshiba Corp | 電子装置及びその装置に含まれる集積回路 |
| EP0545581B1 (en) * | 1991-12-06 | 1999-04-21 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Integrated data processing system including CPU core and parallel, independently operating DSP module |
| FI95980C (fi) * | 1992-09-04 | 1996-04-10 | Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd | Menetelmä ja kytkentäjärjestely ajan mittaamiseksi tarkasti epätarkalla kellolla |
| JPH06139373A (ja) * | 1992-10-27 | 1994-05-20 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| EP0632360A1 (en) * | 1993-06-29 | 1995-01-04 | Xerox Corporation | Reducing computer power consumption by dynamic voltage and frequency variation |
| US5553276A (en) * | 1993-06-30 | 1996-09-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Self-time processor with dynamic clock generator having plurality of tracking elements for outputting sequencing signals to functional units |
| JPH0744266A (ja) * | 1993-08-04 | 1995-02-14 | Canon Inc | デバイス制御装置 |
| JP3490131B2 (ja) * | 1994-01-21 | 2004-01-26 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | データ転送制御方法、データプロセッサ及びデータ処理システム |
| EP0665502B1 (en) * | 1994-01-27 | 2002-06-12 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Asynchronous serial communication circuit |
| EP0666529B1 (en) * | 1994-02-02 | 2004-10-06 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Power management in an asynchronus receiver/transmitter |
| JP3718251B2 (ja) * | 1994-02-28 | 2005-11-24 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | データ処理装置 |
| US5696917A (en) * | 1994-06-03 | 1997-12-09 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for performing burst read operations in an asynchronous nonvolatile memory |
| US5592173A (en) | 1994-07-18 | 1997-01-07 | Trimble Navigation, Ltd | GPS receiver having a low power standby mode |
| JPH08152945A (ja) * | 1994-11-28 | 1996-06-11 | Nec Corp | 消費電力管理装置 |
| JPH08166834A (ja) * | 1994-12-14 | 1996-06-25 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | クロック発生回路及びマイクロコンピュータ |
| KR100255026B1 (ko) * | 1994-12-28 | 2000-05-01 | 디. 크레이그 노룬드 | 마이크로프로세서 및 디버그 시스템 |
| US5842037A (en) | 1995-03-20 | 1998-11-24 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson | Interference reduction in TDM-communication/computing devices |
| US5655100A (en) * | 1995-03-31 | 1997-08-05 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Transaction activation processor for controlling memory transaction execution in a packet switched cache coherent multiprocessor system |
| US5737547A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-04-07 | Microunity Systems Engineering, Inc. | System for placing entries of an outstanding processor request into a free pool after the request is accepted by a corresponding peripheral device |
| US5613235A (en) * | 1995-06-29 | 1997-03-18 | Nokia Mobile Phones Limited | Operation of a radiotelephone in a synchronous extended standby mode for conserving battery power |
| US5774701A (en) | 1995-07-10 | 1998-06-30 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Microprocessor operating at high and low clok frequencies |
| JPH0944277A (ja) * | 1995-07-25 | 1997-02-14 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | マイクロコンピュータ |
| US5964893A (en) | 1995-08-30 | 1999-10-12 | Motorola, Inc. | Data processing system for performing a trace function and method therefor |
| JP3466793B2 (ja) * | 1995-09-28 | 2003-11-17 | 株式会社東芝 | マルチプロセッサシステム |
| US5623234A (en) * | 1996-03-04 | 1997-04-22 | Motorola | Clock system |
| US5724505A (en) | 1996-05-15 | 1998-03-03 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Apparatus and method for real-time program monitoring via a serial interface |
| US5809091A (en) * | 1996-06-04 | 1998-09-15 | Ericsson, Inc. | Timing signal generator for digital communication system |
| US5933627A (en) * | 1996-07-01 | 1999-08-03 | Sun Microsystems | Thread switch on blocked load or store using instruction thread field |
| US5790817A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1998-08-04 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Configurable digital wireless and wired communications system architecture for implementing baseband functionality |
| WO1998019242A1 (fr) * | 1996-10-30 | 1998-05-07 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Processeur de donnees et systeme de traitement de donnees |
| JPH10187300A (ja) * | 1996-12-20 | 1998-07-14 | Sony Corp | 電源制御回路および電源制御方法 |
| JPH10190568A (ja) * | 1996-12-27 | 1998-07-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 無線受信装置 |
| EP0856797B1 (en) | 1997-01-30 | 2003-05-21 | STMicroelectronics Limited | A cache system for concurrent processes |
| US6029061A (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 2000-02-22 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Power saving scheme for a digital wireless communications terminal |
| US6031429A (en) * | 1997-03-19 | 2000-02-29 | Silicon Magic Corporation | Circuit and method for reducing lock-in time in phase-locked and delay-locked loops |
| US6269426B1 (en) * | 1997-06-24 | 2001-07-31 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method for operating a non-blocking hierarchical cache throttle |
| US6052777A (en) * | 1997-06-25 | 2000-04-18 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method for delivering precise traps and interrupts in an out-of-order processor |
| US5963068A (en) * | 1997-07-28 | 1999-10-05 | Motorola Inc. | Fast start-up processor clock generation method and system |
| US6170051B1 (en) * | 1997-08-01 | 2001-01-02 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatus and method for program level parallelism in a VLIW processor |
| US6005904A (en) * | 1997-10-16 | 1999-12-21 | Oasis Design, Inc. | Phase-locked loop with protected output during instances when the phase-locked loop is unlocked |
| US6076157A (en) | 1997-10-23 | 2000-06-13 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus to force a thread switch in a multithreaded processor |
| US5936565A (en) * | 1997-12-10 | 1999-08-10 | Nortel Networks Corporation | Digitally controlled duty cycle integration |
| US6282184B1 (en) * | 1997-12-22 | 2001-08-28 | Nortel Networks Limited | Common digitizing rate for multiple air interfaces for generic cell sites in cellular radio |
| EP0924947A1 (en) | 1997-12-22 | 1999-06-23 | The Technology Partnership Public Limited Company | Power saving in a digital cellular system terminal |
| US6430654B1 (en) * | 1998-01-21 | 2002-08-06 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Apparatus and method for distributed non-blocking multi-level cache |
| EP0939495B1 (en) | 1998-02-26 | 2004-04-14 | Motorola Semiconducteurs S.A. | Power saving system for an electronic portable device |
| US6145122A (en) * | 1998-04-27 | 2000-11-07 | Motorola, Inc. | Development interface for a data processor |
| JPH11312026A (ja) | 1998-04-28 | 1999-11-09 | Nec Corp | クロック信号切替方法およびクロック信号切替システム |
| JP4060442B2 (ja) * | 1998-05-28 | 2008-03-12 | 富士通株式会社 | メモリデバイス |
| JP3786521B2 (ja) * | 1998-07-01 | 2006-06-14 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 半導体集積回路及びデータ処理システム |
| WO2000002118A1 (en) * | 1998-07-02 | 2000-01-13 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Microprocessor |
| US6141762A (en) * | 1998-08-03 | 2000-10-31 | Nicol; Christopher J. | Power reduction in a multiprocessor digital signal processor based on processor load |
| KR100306966B1 (ko) * | 1998-08-04 | 2001-11-30 | 윤종용 | 동기형버스트반도체메모리장치 |
| EP0992906B1 (en) * | 1998-10-06 | 2005-08-03 | Texas Instruments Inc. | Apparatus and method for software breakpoint in a delay slot |
| EP0992907B1 (en) * | 1998-10-06 | 2005-09-28 | Texas Instruments Inc. | Trace fifo management |
| US6255822B1 (en) * | 1998-10-09 | 2001-07-03 | U.S. Philips Corporation | MRI apparatus having a short uniform field magnet with an internal space |
| US6118306A (en) * | 1998-12-03 | 2000-09-12 | Intel Corporation | Changing clock frequency |
| US6763448B1 (en) | 1999-02-16 | 2004-07-13 | Renesas Technology Corp. | Microcomputer and microcomputer system |
| FI106761B (fi) * | 1999-02-19 | 2001-03-30 | Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd | Menetelmä ja piirijärjestely järjestelmien keskinäisen tahdistuksen toteuttamiseksi monimoodilaitteessa |
| US6336168B1 (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2002-01-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method for merging multiple outstanding load miss instructions |
| FR2791217B1 (fr) | 1999-03-18 | 2001-06-01 | Sagem | Procede de veille dans un telephone mobile |
| US6425086B1 (en) * | 1999-04-30 | 2002-07-23 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for dynamic power control of a low power processor |
| US6341347B1 (en) * | 1999-05-11 | 2002-01-22 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Thread switch logic in a multiple-thread processor |
| EP2267597A3 (en) | 1999-05-12 | 2012-01-04 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Digital signal processor having a pipeline structure |
| JP2001022480A (ja) * | 1999-07-09 | 2001-01-26 | Seiko Epson Corp | 情報処理装置 |
| JP2001036958A (ja) * | 1999-07-16 | 2001-02-09 | Nec Corp | 待受け受信方式 |
| US6748475B1 (en) * | 1999-11-05 | 2004-06-08 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Programmable serial port architecture and system |
| EP1226493B1 (en) * | 1999-11-05 | 2006-05-03 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Bus architecture and shared bus arbitration method for a communication processor |
| DE69940473D1 (de) | 1999-11-25 | 2009-04-09 | St Microelectronics Srl | Leseverfahren für nichtflüchtige Speicheranordnung mit automatischer Erkennung eines Burstlesebetriebs sowie entsprechende Leseschaltung |
| EP1103978B1 (en) * | 1999-11-25 | 2009-01-28 | STMicroelectronics S.r.l. | Non-volatile memory device with burst mode reading and corresponding reading method |
| US6205084B1 (en) * | 1999-12-20 | 2001-03-20 | Fujitsu Limited | Burst mode flash memory |
| GB2357602A (en) | 1999-12-22 | 2001-06-27 | Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd | Memory controller for a memory array comprising different memory types |
| US6625740B1 (en) * | 2000-01-13 | 2003-09-23 | Cirrus Logic, Inc. | Dynamically activating and deactivating selected circuit blocks of a data processing integrated circuit during execution of instructions according to power code bits appended to selected instructions |
| US6974437B2 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2005-12-13 | Medtronic Minimed, Inc. | Microprocessor controlled ambulatory medical apparatus with hand held communication device |
| US7143401B2 (en) * | 2000-02-17 | 2006-11-28 | Elbrus International | Single-chip multiprocessor with cycle-precise program scheduling of parallel execution |
| DE10009683A1 (de) * | 2000-02-29 | 2001-08-30 | Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd | Verfahren zum Unterbrechen eines Ruhezustandes einer Kommunikationseinheit in einem Kommunikationssystem, insbesondere in einem Funk-Kommunikationssystem |
| US6421214B1 (en) * | 2000-03-03 | 2002-07-16 | Pass & Seymour, Inc. | Arc fault or ground fault detector with self-test feature |
| JP2001313547A (ja) * | 2000-05-01 | 2001-11-09 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 内部回路へのクロック供給方法およびクロック供給回路 |
| EP1182559B1 (en) * | 2000-08-21 | 2009-01-21 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Improved microprocessor |
| JP2002082832A (ja) * | 2000-09-08 | 2002-03-22 | Nec Corp | キャッシュ更新方法及びキャッシュ更新制御システム並びに記録媒体 |
| US6871292B1 (en) * | 2000-11-20 | 2005-03-22 | Intersil Americas, Inc. | Sequencer and method of selectively inhibiting clock signals to execute reduced instruction sequences in a re-programmable I/O interface |
| US6636225B2 (en) * | 2000-11-20 | 2003-10-21 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Managing texture mapping data in a computer graphics system |
| US6732236B2 (en) * | 2000-12-18 | 2004-05-04 | Redback Networks Inc. | Cache retry request queue |
| SE516758C2 (sv) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-02-26 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Digitalt bussystem |
| US6665776B2 (en) * | 2001-01-04 | 2003-12-16 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. | Apparatus and method for speculative prefetching after data cache misses |
| US6584546B2 (en) * | 2001-01-16 | 2003-06-24 | Gautam Nag Kavipurapu | Highly efficient design of storage array for use in first and second cache spaces and memory subsystems |
| US20020138778A1 (en) * | 2001-03-22 | 2002-09-26 | Cole James R. | Controlling CPU core voltage to reduce power consumption |
| US6968219B2 (en) * | 2001-08-15 | 2005-11-22 | Qualcomm, Incorporated | Method for reducing power consumption in bluetooth and CDMA modes of operation |
| EP1421588B1 (en) * | 2001-08-29 | 2012-01-18 | MediaTek Inc. | Method and apparatus utilizing flash burst mode to improve processor performance |
| US6865503B2 (en) * | 2002-12-24 | 2005-03-08 | Conexant Systems, Inc. | Method and apparatus for telemetered probing of integrated circuit operation |
-
2002
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02768760A patent/EP1421588B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027666 patent/WO2003021409A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02763598A patent/EP1425671B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028169263A patent/CN100570577C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525432A patent/JP2005502114A/ja active Pending
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02773260A patent/EP1421490B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028169689A patent/CN100471079C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/230,534 patent/US7159134B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525468A patent/JP2005502123A/ja active Pending
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027462 patent/WO2003021800A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027684 patent/WO2003021600A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525854A patent/JP4338514B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB02816928XA patent/CN100399472C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02759508A patent/EP1421497B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 AU AU2002331774A patent/AU2002331774A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02759483A patent/EP1421704B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02761537A patent/EP1421465B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/230,528 patent/US6978350B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/230,868 patent/US6768358B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/230,669 patent/US7315956B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60211921T patent/DE60211921T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003526013A patent/JP4340536B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525430A patent/JP4243186B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/231,526 patent/US7114093B2/en active Active
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027758 patent/WO2003021446A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60223051T patent/DE60223051T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60228268T patent/DE60228268D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027669 patent/WO2003021407A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525448A patent/JP3852703B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 EP EP10159945.4A patent/EP2230603B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525475A patent/JP4799819B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CN2009102091339A patent/CN101673238B/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028169271A patent/CN100361109C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60223555T patent/DE60223555T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CN02816976XA patent/CN1549961B/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028169697A patent/CN100451914C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60239347T patent/DE60239347D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027920 patent/WO2003021453A2/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027670 patent/WO2003021439A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028169700A patent/CN100517215C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/230,668 patent/US7007132B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02773259A patent/EP1421463B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 CN CNB028167791A patent/CN1299201C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 WO PCT/US2002/027695 patent/WO2003021426A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-08-29 AU AU2002327599A patent/AU2002327599A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2002-08-29 EP EP02797802.2A patent/EP1499955B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 DE DE60210633T patent/DE60210633T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/231,722 patent/US7174543B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 JP JP2003525461A patent/JP4170218B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-08-29 US US10/231,446 patent/US6889331B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2006
- 2006-07-04 JP JP2006184344A patent/JP4440900B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2007
- 2007-11-15 US US11/985,374 patent/US7698590B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2007-11-15 US US11/985,375 patent/US8156366B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2008
- 2008-10-16 JP JP2008267243A patent/JP2009064456A/ja active Pending
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100517215C (zh) | 用于无线系统中定时及事件处理的方法和装置 | |
| US8799697B2 (en) | Operating system synchronization in loosely coupled multiprocessor system and chips | |
| KR100385155B1 (ko) | 외부핀신호를다중화하는장치를포함하는집적프로세서 | |
| US20070008011A1 (en) | Distributed power and clock management in a computerized system | |
| US20020184547A1 (en) | Device and method for selectively powering down integrated circuit blocks within a system on chip | |
| US10936005B2 (en) | Event controlled clock switching | |
| KR19990006743A (ko) | 데이타처리장치 및 이동체통신단말장치 | |
| US7242230B2 (en) | Microprocessor with power saving clock | |
| CN113986795B (zh) | 一种支持pcie时钟的时钟架构、方法及介质 | |
| JP4482275B2 (ja) | オペレーティングシステムサポートのために一定の時間基準を用いるマルチモード電力管理システムのハードウェアアーキテクチャ | |
| EP2596411B1 (en) | Electronic device with a clock circuit and method for providing an electronic device with a clock signal | |
| Wysocki | Technical background of the Android suspend blockers controversy | |
| WO2006016283A2 (en) | Task scheduling using context switch overhead table | |
| JP3557522B2 (ja) | 割込信号生成装置 | |
| CN114860418A (zh) | 操作系统时钟源的使用方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 | |
| US20120221756A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for adjusting period of clock interruption | |
| JP2004086517A (ja) | デュアルポートメモリのアクセス調停方法 | |
| JP2004110450A (ja) | プロセッサのクロック制御方法および装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right |
Owner name: MEDIATEK INC. Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ANALOG DEVICES INC. Effective date: 20080404 |
|
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TA01 | Transfer of patent application right |
Effective date of registration: 20080404 Address after: Hsinchu Science Industrial Park, Taiwan Applicant after: MEDIATEK Inc. Address before: Massachusetts, USA Applicant before: ANALOG DEVICES, Inc. |
|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Granted publication date: 20090722 |