EP1157689B1 - Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers - Google Patents
Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1157689B1 EP1157689B1 EP01112230A EP01112230A EP1157689B1 EP 1157689 B1 EP1157689 B1 EP 1157689B1 EP 01112230 A EP01112230 A EP 01112230A EP 01112230 A EP01112230 A EP 01112230A EP 1157689 B1 EP1157689 B1 EP 1157689B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- hfa
- formoterol
- solution
- ethanol
- formulations
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Revoked
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/10—Dispersions; Emulsions
- A61K9/12—Aerosols; Foams
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/0012—Galenical forms characterised by the site of application
- A61K9/007—Pulmonary tract; Aromatherapy
- A61K9/0073—Sprays or powders for inhalation; Aerolised or nebulised preparations generated by other means than thermal energy
- A61K9/008—Sprays or powders for inhalation; Aerolised or nebulised preparations generated by other means than thermal energy comprising drug dissolved or suspended in liquid propellant for inhalation via a pressurized metered dose inhaler [MDI]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/16—Amides, e.g. hydroxamic acids
- A61K31/165—Amides, e.g. hydroxamic acids having aromatic rings, e.g. colchicine, atenolol, progabide
- A61K31/167—Amides, e.g. hydroxamic acids having aromatic rings, e.g. colchicine, atenolol, progabide having the nitrogen of a carboxamide group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. lidocaine, paracetamol
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/439—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom the ring forming part of a bridged ring system, e.g. quinuclidine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/47—Quinolines; Isoquinolines
- A61K31/4738—Quinolines; Isoquinolines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4745—Quinolines; Isoquinolines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems condensed with ring systems having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. phenantrolines
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/535—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines
- A61K31/5375—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine
- A61K31/5386—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/56—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/56—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids
- A61K31/57—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane or progesterone
- A61K31/573—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane or progesterone substituted in position 21, e.g. cortisone, dexamethasone, prednisone or aldosterone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K45/00—Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
- A61K45/06—Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/10—Dispersions; Emulsions
- A61K9/12—Aerosols; Foams
- A61K9/124—Aerosols; Foams characterised by the propellant
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/08—Bronchodilators
Definitions
- the invention relates to stable pharmaceutical solutions to be used with pressurised metered dose inhalers (MDIs) suitable for aerosol administration.
- MDIs pressurised metered dose inhalers
- the invention relates to solutions to be used with pressurised metered dose inhalers (MDIs) suitable for aerosol administration containing formoterol fumarate (a ⁇ 2 -agonist) and being stable at room temperature for a pharmaceutically acceptable shelf-life.
- Pressurised metered dose inhalers are well known devices for administering pharmaceutical products to the respiratory tract by inhalation.
- Drugs commonly delivered by inhalation include bronchodilators such as ⁇ 2 -agonists and anticholinergics, corticosteroids, anti-leukotrienes, anti-allergics and other materials that may be efficiently administered by inhalation, thus increasing the therapeutic index and reducing side effects of the active material.
- bronchodilators such as ⁇ 2 -agonists and anticholinergics, corticosteroids, anti-leukotrienes, anti-allergics and other materials that may be efficiently administered by inhalation, thus increasing the therapeutic index and reducing side effects of the active material.
- MDI uses a propellant to expel droplets containing the pharmaceutical product to the respiratory tract as an aerosol.
- Formulations for aerosol administration via MDIs can be solutions or suspensions.
- Solution formulations offer the advantage of being homogeneous with the active ingredient and excipients completely dissolved in the propellant vehicle or its mixture with suitable co-solvents such as ethanol. Solution formulations also obviate physical stability problems associated with suspension formulations so assuring more consistent uniform dosage administration.
- the preferred propellants used in aerosols for pharmaceutical use have been a group of chlorofluorocarbons which are commonly called Freons or CFCs, such as CCl 3 F (Freon 11 or CFC-11), CCl 2 F 2 (Freon 12 or CFC-12), and CClF 2 -CClF 2 (Freon 114 or CFC-114).
- Freons or CFCs such as CCl 3 F (Freon 11 or CFC-11), CCl 2 F 2 (Freon 12 or CFC-12), and CClF 2 -CClF 2 (Freon 114 or CFC-114).
- CFC chlorofluorocarbon
- Hydrofluoroalkanes (HFAs) known also as hydro-fluoro-carbons (HFCs)] contain no chlorine and are considered less destructive to ozone and these are proposed as substitutes for CFCs.
- HFAs and in particular 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFA 134a) and 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane (HFA 227) have been acknowledged to be the best candidates for non-CFC propellants and a number of medicinal aerosol formulations using such HFA propellant systems have been disclosed.
- HFA solution formulations may suffer to a greater extent of chemical stability problems with respect to the corresponding CFC formulations.
- TA 2005 8-hydroxy-5-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(1R)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl] amino] ethyl]-2(1H)-quinolinone
- TA 2005 8-hydroxy-5-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(1R)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl] amino] ethyl]-2(1H)-quinolinone
- salbutamol albuterol
- the currently marketed CFC solution formulation exhibits a limited shelf life, i.e. 12 months at refrigerator temperature, 4 ⁇ 2°C, and only 3 month at room temperature.
- an aerosol composition which comprises as active ingredient formoterol fumarate in a solution of a liquefied HFA 134a propellant and ethanol as co-solvent, and hydrochloric acid in an amount such that the solution has an apparent pH between 3.0 and 3.5.
- the composition comprises 1.0 M hydrochloric acid in an amount between 3 and 3.5 ⁇ l per 1.44 mg formoterol fumarate in 12 mL of the composition.
- the composition of the invention shall be contained in a pressurised MDI having part or all of its internal metallic surfaces made of stainless steel, anodised aluminium or lined with an inert organic coating.
- inert containers allows to avoid the leaching of metal ions or alkali as a consequence of the action of the acid contained in the formulation onto the inner walls of the cans.
- Metal ions such Al 3+ or alkali respectively deriving from the conventional aluminium or glass cans could in turn catalyse radical oxidative or other chemical reactions of the active ingredient which give rise to the formation of degradation products.
- a pressurised MDI for administering pharmaceutical doses consisting of an anodised aluminium container filled with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a solution of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a as a propellant in turn containing 12% w / w ethanol as a co-solvent and optionally isopropyl myristate as a low volatility component in an amount less/equal than 1.0% w/w, the apparent pH of said solution having been adjusted to between 3.0 and 3.5 by addition of small amounts of hydrochloric acid.
- the expression '% w/w' means the weight percentage of the component in respect to the total weight of the composition.
- the low volatility component besides increasing the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) of the aerosol particles on actuation of the inhaler as explained in the following, further improves the stability of the formulation.
- MMAD mass median aerodynamic diameter
- the addition of a low volatility component with a reduced polarity with respect to the co-solvent such as an ester may allow either to reduce the amount of acid to be added for adjusting the pH and diminish the polarity of the medium so limiting the possible uptake of environmental water.
- the shelf-life of the formulation put in the device of the invention could be predicted to be greater than two years at the refrigerator temperature (4-10° C) and three months at room temperature.
- a pressurised MDI consisting of a coated container filled with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a solution of a combination of formoterol fumarate and beclometasone dipropionate (hereinafter BDP) in HFA 134a as a propellant in turn containing 12% w / w ethanol as a co-solvent with or without isopropyl myristate as low volatility component, the apparent pH of said solution having been adjusted to between 3.0 and 3.5 by addition of small amounts of hydrochloric acid.
- BDP beclometasone dipropionate
- WO 97/47286 EP 513127 , EP 504112 , WO 93/11747 , WO 94/21228 , WO 94/21229 , WO 96/18384 , WO 96/19198 , WO 96/19968 , WO 98/05302 , WO 98/34595 and WO 00/07567 disclose HFA formulations in the form of suspensions in which ⁇ 2 -agonists such formoterol and salbutamol are either exemplified and/or claimed.
- WO 99/65464 refers to HFA formulations containg two or more active ingredients in which at least one is in suspension.
- the preferred formulations comprises salbutamol sulphate in suspension.
- WO 98/34596 the applicant described solution compositions for use in an aerosol inhaler, comprising an active material, a propellant containing a hydrofluoroalkane (HFA), a cosolvent and further comprising a low volatility component to increase the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) of the aerosol particles on actuation of the inhaler.
- HFA hydrofluoroalkane
- MMAD mass median aerodynamic diameter
- pressurised MDI's for dispensing solution of an active ingredient in a hydrofluorocarbon propellant, a co-solvent and optionally a low-volatility component characterized in that part or all of the internal surfaces of said inhalers consist of stainless steel, anodised aluminium or are lined with an inert organic coating.
- the examples are referred only to steroids and anticholinergic agents.
- the use of coated containers, even in the presence of an organic acid is not sufficient for providing stable solution formulations of a phenylalkylamino derivative such as salbutamol.
- EP 673240 proposes the use of acids as stabilisers preventing the chemical degradation of the active ingredient in aerosol solution formulations comprising HFAs.
- Most examples relate to ipratropium bromide, an anticholinergic drug and only an example is presented for a ⁇ 2 -agonist, i.e. fenoterol.
- fenoterol a ⁇ 2 -agonist
- salbutamol is claimed, no exemplary formulations are provided.
- the stability data are reported only for ipratropium and the patentee does not either make difference between the use of organic and inorganic acids. It is indeed evident from the data reported in the example 1 of the present application, that salbutamol cannot be stabilised at all by addition of organic acids even when stored in coated cans.
- WO 98/34596 refers to solution formulations containing a propellant and a physiologically acceptable polymer which could help the solubilisation and the stability as well of the active ingredients.
- WO 00/06121 refers to propellant mixtures for aerosol dinitrogen monoxide and a hydrofluoroalkane in the preparation of suspension and solution aerosols.
- the use of dinitrogen monoxide may improve the stability at storage of oxidation-sensitive active ingredients.
- ⁇ 2 -agonist such as levosalbutamol sulphate, formoterol fumarate and salmeterol xinafoate, only examples referred to suspensions are reported.
- WO 99/65460 claims pressurised MDI's containing stable formulations of a ⁇ -agonist drug in suspension or solution.
- Examples refer to solutions of formoterol fumarate containing an HFA propellant and ethanol as co-solvent, filled in conventional aluminium or plastic coated glass cans.
- the method of filling an aerosol inhaler with a composition of the invention comprises:
- the active ingredient which is used in the aerosol compositions of the invention is formoterol fumarate which may be used in combinations with steroids such as beclomethasone dipropionate, fluticasone propionate, budesonide and its 22R-epimer or with anticholinergic atropine-like derivatives such as ipratropium bromide, oxitropium bromide, tiotropium bromide.
- steroids such as beclomethasone dipropionate, fluticasone propionate, budesonide and its 22R-epimer or with anticholinergic atropine-like derivatives such as ipratropium bromide, oxitropium bromide, tiotropium bromide.
- the active ingredient is a long acting ⁇ 2 -agonist belonging to the formula sketched below wherein R is 1-formylamino-2-hydroxy- phen-5-yl (formoterol).
- R is 1-formylamino-2-hydroxy- phen-5-yl (formoterol).
- the formulation to be suitable for delivering a therapeutic amount of the active ingredient in one or two actuations.
- the formulation will be suitable for delivering 6-12 ⁇ g/dose of formoterol fumarate either alone or in combination.
- dose we mean the amount of active ingredient delivered by a single actuation of the inhaler.
- the formulations of the invention will be contained in cans having part of all of the internal surfaces made of anodised aluminium, stainless steel or lined with an inert organic coating.
- preferred coatings are epoxy-phenol resins, perfluoroalkoxyalkane, perfluoroalkoxyalkylene, perfluoroalkylenes such as polytetrafluoroethylene, fluorinated-ethylene-propylene, polyether sulfone and a copolymer fluorinated-ethylene-propylene polyether sulfone.
- Other suitable coatings could be polyamide, polyimide, polyamideimide, polyphenylene sulfide or their combinations.
- cans having a rolled-in rim and preferably a part or full rollover rim are used.
- the formulation is actuated by a metering valve capable of delivering a volume of between 50 ⁇ l and 100 ⁇ l.
- Metering valves fitted with gaskets made of chloroprene-based rubbers can preferably be used to reduce the ingress of moisture which, as previously mentioned, can adversely affect the stability of the drug during storage.
- further protection can be achieved by packaging the product in a sealed aluminium pouch.
- the hydrofluorocarbon propellant is HFA 134a.
- the co-solvent is ethanol.
- the low volatility component when present, has a vapour pressure at 25°C lower than 0.1 kPa, preferably lower than 0.05 kPa.
- it could be selected from the group of glycols, particularly propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol and glycerol or esters, for example ascorbyl palmitate, isopropyl myristate and tocopherol esters.
- compositions of the invention may contain from 0.1 to 10% w/w of said low volatility component, preferably between 0.3 to 5% w/w, more preferably between 0.4 and 2.0% w/w.
- Propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, glycerol with residual water less than 0.1% w/w and esters of long-chain fatty acids are the preferred low-volatility components. More preferred are those with a dipole moment less than 2.0 or with a dielectric static constant less than 20, preferably less than 10. Particularly preferred is isopropyl myristate.
- the function of the low volatility component is to modulate the MMAD of the aerosol particles and optionally to further improve the stability of the formulation.
- particularly preferred is the use of isopropyl myristate.
- the apparent pH range is comprised between 3.0 and 3.5.
- the strong mineral acid hydrochloric acid is used to adjust the apparent pH.
- the amount of acid to be added to reach the desired apparent pH will be pre-determined in the model vehicle reported before and it will depend on the type and concentration of the active ingredient.
- an amount comprised between 3 and 3.5 ⁇ l of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid should be added.
- Solution formulations were prepared by dissolving 1.44 mg of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a in turn containing 15% w/w ethanol and 1.3% w/w glycerol.
- pMDIs were stored upright over the range 4-50°C for up to 28 days.
- Formoterol content was determined by HPLC and the percent residual concentrations calculated relative to the 12 ⁇ g/shot nominal dose. The percent residual formoterol concentration is reported in Table 2.
- Derived Arrhenius parameters were used to estimate rate constants at ambient temperature (18-25°) and solutions stored in a domestic refrigerator (4-10°); these rate constants were used to calculate predicted shelf-life for 5% and 10% degradation of formoterol (Table 3).
- Table 3 The calculated shelf-life data in Table 3 indicates that formoterol is not stable in this HFA 134a-ethanol-glycerol vehicle.
- Table 2 Degradation Rate Data for Formoterol-HFA 134a pMDI Solutions (12 ⁇ g/100 ⁇ l) Vehicle: HFA 134a with 1.3% w/w Glycerol, 15.0% w/w Ethanol Epoxy-phenol lacquered cans stored upright Time (days) Percent Residual Conc.
- Table 4 pH' and Formoterol Content of Formoterol-Vertrel XF/HFA Solutions (12 ⁇ g/100 ⁇ l) Vehicle: Vertrel XF/HFA with 20% Ethanol and Hydrochloric Acid St Gobain glass vials stored upright Acidity Function (pH') Percent Residual Conc.
- Formoterol 40 days Initial 10 days 20 days 1.8 2.8 100 4.8 Nil 2.1 4.4 100 75.1 70.7 2.6 4.2 100 97.2 86.7 3.3 4.2 100 97.1 89.9 5.6 6.6 100 95.8 92.1 7.4 6.7 100 85.4 67.2
- Formoterol formulations (12 ⁇ g/100 ⁇ l) were prepared by dissolving 1.44 mg of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a containing 12% w / w ethanol with and without 1.0% w / w isopropyl myristate. The latter was included as a non-volatile excipient with the potential for increasing MMAD if so desired. It also improves the solubility of formoterol in the vehicle and reduces polarity of the vehicle compared to the addition of glycerol.
- pMDI cans containing 3.1-3.4 ⁇ l 1.0 M hydrochloric acid were set down on storage, upright and inverted, at 4°C to 50°C and samples taken for analysis of formoterol content at appropriate intervals.
- a matrix of formulations containing 1.44 mg (12 ⁇ g/100 ⁇ l) formoterol fumarate were prepared in HFA 134a containing 12.0% w / w ethanol with or without 1.0% w / w isopropyl myristate as non-volatile excipient. Aliquots of drug concentrate were transferred to anodised cans and 3.15-3.35 ⁇ l of 1.0M hydrochloric acid added prior to crimping with 50 ⁇ l valves and gassing between 22 and 28 replicates at each acid strength were prepared.
- Table 5 shows the results obtained at 40° and 50° after 11-40 day's storage. Each value (expressed as per cent nominal drug concentration) is obtained from a different can.
- pMDI coated cans containing 3.25 ⁇ l 1.0 M hydrochloric acid were set down on storage inverted, at 4°C and samples taken for analysis of formoterol and BDP contents at appropriate intervals.
Description
- The invention relates to stable pharmaceutical solutions to be used with pressurised metered dose inhalers (MDIs) suitable for aerosol administration. In particular, the invention relates to solutions to be used with pressurised metered dose inhalers (MDIs) suitable for aerosol administration containing formoterol fumarate (a β2-agonist) and being stable at room temperature for a pharmaceutically acceptable shelf-life.
- Pressurised metered dose inhalers are well known devices for administering pharmaceutical products to the respiratory tract by inhalation.
- Drugs commonly delivered by inhalation include bronchodilators such as β2-agonists and anticholinergics, corticosteroids, anti-leukotrienes, anti-allergics and other materials that may be efficiently administered by inhalation, thus increasing the therapeutic index and reducing side effects of the active material.
- MDI uses a propellant to expel droplets containing the pharmaceutical product to the respiratory tract as an aerosol. Formulations for aerosol administration via MDIs can be solutions or suspensions. Solution formulations offer the advantage of being homogeneous with the active ingredient and excipients completely dissolved in the propellant vehicle or its mixture with suitable co-solvents such as ethanol. Solution formulations also obviate physical stability problems associated with suspension formulations so assuring more consistent uniform dosage administration.
- For many years the preferred propellants used in aerosols for pharmaceutical use have been a group of chlorofluorocarbons which are commonly called Freons or CFCs, such as CCl3F (Freon 11 or CFC-11), CCl2F2 (Freon 12 or CFC-12), and CClF2-CClF2 (Freon 114 or CFC-114).
- Recently, the chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) propellants such as Freon 11 and Freon 12 have been implicated in the destruction of the ozone layer and their production is being phased out.
- Hydrofluoroalkanes [(HFAs) known also as hydro-fluoro-carbons (HFCs)] contain no chlorine and are considered less destructive to ozone and these are proposed as substitutes for CFCs.
- HFAs and in particular 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFA 134a) and 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane (HFA 227) have been acknowledged to be the best candidates for non-CFC propellants and a number of medicinal aerosol formulations using such HFA propellant systems have been disclosed.
- Due to the higher polarity of the HFA propellants, in particular of HFA 134a (dielectric constant D ≥ 9.5), with respect to CFC vehicles (D ≤2.3), HFA solution formulations may suffer to a greater extent of chemical stability problems with respect to the corresponding CFC formulations.
- Preparation of stable HFA solution formulations is even more critical when bronchodilator β2-agonists belonging to the class of the phenylalkylamino derivatives are concerned; said drugs, like formoterol, 8-hydroxy-5-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(1R)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl] amino] ethyl]-2(1H)-quinolinone (hereinafter referred as TA 2005), and salbutamol (albuterol) and others, may suffer of inherent chemical stability problems due to their susceptibility to oxidative conditions; moreover, in the view of the presence of some functional groups like formamide, a higher polarity of the vehicle may accelerate the rate of solvolysis reactions.
- As far as formoterol, the currently marketed CFC solution formulation (Foradil®) exhibits a limited shelf life, i.e. 12 months at refrigerator temperature, 4± 2°C, and only 3 month at room temperature.
- In consideration of the problems outlined, it would be highly advantageous to provide a formulation in the form ofa HFA solution to be administered by MDIs aimed at providing pharmaceutical doses of formoterol fumarate characterised by adequate shelf-life
- It is an object of the invention to provide a formulation in the form of HFA solution to be administered by MDI's for providing pharmaceutical doses of formoterol fumarate into the low respiratory tract of patients suffering of pulmonary diseases such as asthma, characterised by adequate shelf-life. In particular, it is an object of the invention to provide a formulation in the form of HFA solution to be administered by MDIs for providing pharmaceutical doses of formoterol with a greater shelf-life of that of the formulation currently on the market.
- According to the invention there is provided an aerosol composition which comprises as active ingredient formoterol fumarate in a solution of a liquefied HFA 134a propellant and ethanol as co-solvent, and hydrochloric acid in an amount such that the solution has an apparent pH between 3.0 and 3.5. In a particular embodiment, the composition comprises 1.0 M hydrochloric acid in an amount between 3 and 3.5 µl per 1.44 mg formoterol fumarate in 12 mL of the composition. The composition of the invention shall be contained in a pressurised MDI having part or all of its internal metallic surfaces made of stainless steel, anodised aluminium or lined with an inert organic coating.
- In fact, it has been found that, in the case of certain active ingredients such as β2-agonists, their chemical stability in HFA solution formulations could be dramatically improved by a proper and combined selection of the kind of cans as well as the apparent pH range. The attribution 'apparent' is used as pH is indeed characteristic of aqueous liquids where water is the dominant component (Mole Fraction > 0.95). In relatively aprotic solvents such as the HFA-ethanol vehicles used in these studies, protons are non-hydrated; their activity coefficients differ significantly from those in aqueous solution. Although the Nernst equation with respect to EMF applies and the pH-meter glass electrode system will generate a variable milli-volt output according to proton concentration and vehicle polarity, the "pH" meter reading is not a true pH value. The meter reading represents an apparent pH or acidity function (pH').
- When formoterol fumarate was titrated with a strong acid in a model vehicle system commercially available (HFA 43-10MEE, Vertrel XF, Dupont), according to a method developed by the applicant, the pH' profile exhibits a shallow negative to about pH' = 5.5; thereafter the acidity function drops abruptly. Surprisingly the corresponding HFA formulations turned out to much more stable below pH' 5.5.
- On the other hand, the use of inert containers allows to avoid the leaching of metal ions or alkali as a consequence of the action of the acid contained in the formulation onto the inner walls of the cans. Metal ions such Al3+ or alkali respectively deriving from the conventional aluminium or glass cans could in turn catalyse radical oxidative or other chemical reactions of the active ingredient which give rise to the formation of degradation products.
- In the case of active ingredients such as formoterol, it is well known that humidity could be detrimental to the stability of the active ingredient during storage. According to a particular embodiment of the invention, there is provided a pressurised MDI for administering pharmaceutical doses consisting of an anodised aluminium container filled with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a solution of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a as a propellant in turn containing 12% w/w ethanol as a co-solvent and optionally isopropyl myristate as a low volatility component in an amount less/equal than 1.0% w/w, the apparent pH of said solution having been adjusted to between 3.0 and 3.5 by addition of small amounts of hydrochloric acid. The expression '% w/w' means the weight percentage of the component in respect to the total weight of the composition.
- The low volatility component besides increasing the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) of the aerosol particles on actuation of the inhaler as explained in the following, further improves the stability of the formulation. In fact, the addition of a low volatility component with a reduced polarity with respect to the co-solvent such as an ester may allow either to reduce the amount of acid to be added for adjusting the pH and diminish the polarity of the medium so limiting the possible uptake of environmental water.
- The shelf-life of the formulation put in the device of the invention could be predicted to be greater than two years at the refrigerator temperature (4-10° C) and three months at room temperature.
- According to another particular embodiment of the invention, there is provided a pressurised MDI consisting of a coated container filled with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a solution of a combination of formoterol fumarate and beclometasone dipropionate (hereinafter BDP) in HFA 134a as a propellant in turn containing 12% w/w ethanol as a co-solvent with or without isopropyl myristate as low volatility component, the apparent pH of said solution having been adjusted to between 3.0 and 3.5 by addition of small amounts of hydrochloric acid.
- However, a person sufficiently skilled in the art can easily apply the teaching of the present invention to the preparation of HFA solution formulations containing other active ingredients bearing functional groupssensitive to hydrolytic and/or oxidative reactions, such as formamide and cathecol respectively.
-
WO 97/47286 EP 513127 EP 504112 WO 93/11747 WO 94/21228 WO 94/21229 WO 96/18384 WO 96/19198 WO 96/19968 WO 98/05302 WO 98/34595 WO 00/07567 -
WO 99/65464 - In
WO 98/34596 - In the international application n°
PCT/EP99/09002 filed on 23/11/99 published on June 2, 2000 asWO 00/30608 -
EP 673240 EP 673240 page 5, lines 15 to 16 which says that an amount of inorganic acid should be added to obtain a pH value from 1 to 7, so a very broad and generic range. -
WO 98/34596 -
WO 00/06121 -
WO 99/65460 - Samples stored under accelerated conditions (40° C, 75% relative humidity) for a very short period, one month, exhibited about 10% loss of drug. According to pharmaceutical guidelines on stability, loss of 10% of active ingredient does not meet the criteria of acceptance. Moreover, as it is evident from the data reported in Example 2 of the present application, following the teaching of
WO 99/65460 - The method of filling an aerosol inhaler with a composition of the invention comprises:
- (a) Preparation of a solution of formoterol fumarate, and optionally one or more active ingredients in ethanol, and optionally one or more co-solvents optionally containing an appropriate amount of a low volatility component
- (b) Filling of the device with said solution
- (c) Adding a pre-determined amount of a strong mineral acid
- (d) Adding a propellant containing a hydrofluoroalkane (HFA)
- (e) Crimping with valves and gassing
- The active ingredient which is used in the aerosol compositions of the invention is formoterol fumarate which may be used in combinations with steroids such as beclomethasone dipropionate, fluticasone propionate, budesonide and its 22R-epimer or with anticholinergic atropine-like derivatives such as ipratropium bromide, oxitropium bromide, tiotropium bromide.
- The active ingredient is a long acting β2-agonist belonging to the formula sketched below
Although the preferred formulations of the invention are in the form of solutions, in case of the combinations, one of the two active ingredients could be present in suspension. - We prefer the formulation to be suitable for delivering a therapeutic amount of the active ingredient in one or two actuations. Preferably the formulation will be suitable for delivering 6-12 µg/dose of formoterol fumarate either alone or in combination.
For "dose" we mean the amount of active ingredient delivered by a single actuation of the inhaler. - The formulations of the invention will be contained in cans having part of all of the internal surfaces made of anodised aluminium, stainless steel or lined with an inert organic coating. Examples of preferred coatings are epoxy-phenol resins, perfluoroalkoxyalkane, perfluoroalkoxyalkylene, perfluoroalkylenes such as polytetrafluoroethylene, fluorinated-ethylene-propylene, polyether sulfone and a copolymer fluorinated-ethylene-propylene polyether sulfone. Other suitable coatings could be polyamide, polyimide, polyamideimide, polyphenylene sulfide or their combinations.
- To further improve the stability, cans having a rolled-in rim and preferably a part or full rollover rim are used.
- The formulation is actuated by a metering valve capable of delivering a volume of between 50 µl and 100 µl.
- Metering valves fitted with gaskets made of chloroprene-based rubbers can preferably be used to reduce the ingress of moisture which, as previously mentioned, can adversely affect the stability of the drug during storage. Optionally, further protection can be achieved by packaging the product in a sealed aluminium pouch.
- The hydrofluorocarbon propellant is HFA 134a.
- The co-solvent is ethanol.
- The low volatility component, when present, has a vapour pressure at 25°C lower than 0.1 kPa, preferably lower than 0.05 kPa. Advantageously, it could be selected from the group of glycols, particularly propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol and glycerol or esters, for example ascorbyl palmitate, isopropyl myristate and tocopherol esters.
- The compositions of the invention may contain from 0.1 to 10% w/w of said low volatility component, preferably between 0.3 to 5% w/w, more preferably between 0.4 and 2.0% w/w.
- Propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, glycerol with residual water less than 0.1% w/w and esters of long-chain fatty acids are the preferred low-volatility components. More preferred are those with a dipole moment less than 2.0 or with a dielectric static constant less than 20, preferably less than 10. Particularly preferred is isopropyl myristate.
- The function of the low volatility component is to modulate the MMAD of the aerosol particles and optionally to further improve the stability of the formulation. With respect to the latter aspect, particularly preferred is the use of isopropyl myristate.
- The apparent pH range is comprised between 3.0 and 3.5.
- The strong mineral acid hydrochloric acid is used to adjust the apparent pH.
- The amount of acid to be added to reach the desired apparent pH will be pre-determined in the model vehicle reported before and it will depend on the type and concentration of the active ingredient. In the case of the formulations of formoterol fumarate and its combination with beclometasone dipropionate, an amount comprised between 3 and 3.5 µl of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid should be added.
- The following examples further illustrate the invention.
- Compositions containing 24 mg of salbutamol (100 µg/dose), 10-20% (w/w) ethanol in HFA 134a put in 12 mL epoxy phenol resin lacquered cans, with or without addition of different organic acids, were stored at 40- 50° C.
- The results in term of stability expressed as percentage of remaining drug determined by HPLC, are reported in Table 1.
Table 1 % SALBUTAMOL Acid t = 42 days t= 1.5 months at 4° C None 69% - Oleic 69-70% - Xinafoic 70% - Citric (0.41 w/w) - 40.0 Citric (0.02 w/w) - 55,1 30% Acetic acid (0.4% w/w) - 49.6 30% Acetic acid (0.14% w/w) - 73.8 - The results show that the addition of organic acids does not improve the stability of salbutamol even when coated cans are used.
- Solution formulations were prepared by dissolving 1.44 mg of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a in turn containing 15% w/w ethanol and 1.3% w/w glycerol. pMDIs were stored upright over the range 4-50°C for up to 28 days. Formoterol content was determined by HPLC and the percent residual concentrations calculated relative to the 12µg/shot nominal dose. The percent residual formoterol concentration is reported in Table 2. Derived Arrhenius parameters were used to estimate rate constants at ambient temperature (18-25°) and solutions stored in a domestic refrigerator (4-10°); these rate constants were used to calculate predicted shelf-life for 5% and 10% degradation of formoterol (Table 3).
- The calculated shelf-life data in Table 3 indicates that formoterol is not stable in this HFA 134a-ethanol-glycerol vehicle.
Table 2: Degradation Rate Data for Formoterol-HFA 134a pMDI Solutions (12µg/100µl) Vehicle: HFA 134a with 1.3% w/w Glycerol, 15.0% w/w Ethanol Epoxy-phenol lacquered cans stored upright Time (days) Percent Residual Conc. Formoterol 50°C 43°C 40°C 25° C 4°C Initial 99.7 99.7 99.7 99.7 99.7 2 92.5 - - - - 4 87.2 89.4 - - - 6 80.6 - - - - 7 - - 89.0 - - 10 74.9 - - - - 12 72.1 79.4 - - - 14 67.0 - 81.7 92.0 - 16 64.4 75.7 - - - 18 59.5 - - - - 20 59.5 74.5 - - - 24 54.6 68.6 - - - 28 47.2 63.3 71.3 86.6 96.7 r 0.995 0.989 0.993 0.997 - Rate Constant 2.53 1.49 1.17 0.51 0.11 (day-1 x 102) Arrhenius Plot Parameters: K = AeE/RT A = 2.28 x 106 day-1 : E = 49.4 kJ mol-1; r = 0.9985 Table 3: Predicted Shelf Life Data for Formoterol-HFA 134a pMDI Solutions (12µg/100µl) Vehicle: HFA 134a with 1.3% w/w Glycerol, 15% w/w Ethanol Epoxy-phenol lacquered cans stored upright Temperature Rate Constant
(day-1 x 103)Shelf-Life (days) t 10% t 5% 4°C 1.10 95 47 10°C 1.74 60 29 20°C 3.51 30 15 25°C 4.93 21 10 -
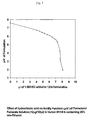
- (a) 1.0 M hydrochloric acid was added incrementally to 50 mL of HFA 43-10MEE (Vertrel XF) containing 20% w/w ethanol and pH' measured after each aliquot of acid.
Figure 1 shows the resultant titration curve normalised to the usual fill volume of a pMDI can (12 L). The pH' profile exhibits a shallow negative slope to about pH'=5.5; thereafter the acidity function drops abruptly. - (b) Experiment (a) was repeated with formoterol formulations containing a lower concentration of ethanol (12% w/w) and with the addition of 1.0% isopropyl myristate. The resultant pH profile, for replicate bulk solutions, shown in
Figure 2 is similar in shape with the abrupt fall in pH' per unit increment of acid again commencing at about pH' = 5.5. However, only about half the acid is required to achieve the same reduction in pH'. This is largely due to the reduction in ethanol content;Figure 2 also shows similarity in the profiles obtained with and without isopropyl myristate. - Aliquots of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid were added to 12 mL of formoterol solution in glass vials. After measurement of pH, valves were crimped on and the vials stored upright at 50°C. Vial samples containing different concentrations of acid were assayed for residual formoterol after 10 and 20 days storage. The pH' of a third vial was determined after 40 days storage. Results are shown in Table 4. Table 4 shows changes in pH on storage; this is probably largely associated with leaching of alkali from the soft glass of the vials. However, overall consideration of the pH' and formoterol content data implies that the stability of a solution formulation of the drug in HFA can be improved by the addition of mineral acid to provide a formulation with pH' between 2.5-5.0.
Table 4: pH' and Formoterol Content of Formoterol-Vertrel XF/HFA Solutions (12µg/100µl) Vehicle: Vertrel XF/HFA with 20% Ethanol and Hydrochloric Acid St Gobain glass vials stored upright Acidity Function (pH') Percent Residual Conc. Formoterol Initial 40 days Initial 10 days 20 days 1.8 2.8 100 4.8 Nil 2.1 4.4 100 75.1 70.7 2.6 4.2 100 97.2 86.7 3.3 4.2 100 97.1 89.9 5.6 6.6 100 95.8 92.1 7.4 6.7 100 85.4 67.2 - Formoterol formulations (12µg/100µl) were prepared by dissolving 1.44 mg of formoterol fumarate in HFA 134a containing 12% w/w ethanol with and without 1.0% w/w isopropyl myristate. The latter was included as a non-volatile excipient with the potential for increasing MMAD if so desired. It also improves the solubility of formoterol in the vehicle and reduces polarity of the vehicle compared to the addition of glycerol.
- pMDI cans containing 3.1-3.4µl 1.0 M hydrochloric acid were set down on storage, upright and inverted, at 4°C to 50°C and samples taken for analysis of formoterol content at appropriate intervals.
- Stability data obtained after 70 days of storage are given in Table 5.
- A matrix of formulations containing 1.44 mg (12µg/100µl) formoterol fumarate were prepared in HFA 134a containing 12.0% w/w ethanol with or without 1.0% w/w isopropyl myristate as non-volatile excipient. Aliquots of drug concentrate were transferred to anodised cans and 3.15-3.35 µl of 1.0M hydrochloric acid added prior to crimping with 50µl valves and gassing between 22 and 28 replicates at each acid strength were prepared.
- To determine residual formoterol, 30 x 50µl shots were discharges into DUSA tubes. The acid range selected was anticipated to give pH' values of 3.0-3.5 and to determine the formulation sensitivity to small changes in acid concentration. Cans were placed on stored upright and inverted (valve up and down respectively) at 25-50°C.
- Table 5 shows the results obtained at 40° and 50° after 11-40 day's storage. Each value (expressed as per cent nominal drug concentration) is obtained from a different can.
- Initial values were obtained for two cans of each acid strength. Inspection of the data shows all assay values to within the reproducibility of the HPLC assay and independent of acid strength. A similar conclusion was drawn for the storage time point replicates, i.e., independent of acid strength (3.2-3.3µl) or whether cans were stored upright or inverted. Consequently for kinetics calculation the mean value for initial (n=10) and subsequent time points (n=6) was used.
- In Table 6 are reported the Arrhenius parameters together with estimated shelf lives at 4, 10 and 25°C. The t5% is predicted to be greater than 3 months at ambient temperature and approximately 2 years at 4°C.
Table 5: Stability Data for Formoterol Fumarate Solutions (12µg/100µl) in HFA 134a containing 12.0% Ethanol ± 1.0% Isopropyl Myristate (values are expressed as percent nominal) Anodised cans fitted with 50µl valves/30 doses collected per can Different cans assessed at each condition Cans stored upright (* inverted) 1.0M HCl
µl per CanSTORAGE CONDITION/No isopropyl myristate Initial 40°C; 40 days 50°C; 11 days 50°C; 33 days 1st Can 2nd Can 1st Can 2nd Can 1st Can 2ndCan 1stCan 2nd Can 3.15 99.8 99.6 - - - - - - 3.20 100.8 99.7 96.0 93.2* 96.7 96.5 88.5 89.9* 3.25 97.9 98.8 93.9 94.3* 96.4 96.5 92.2 91.5* 3.30 97.3 98.9 93.7 93.7* 97.0 89.1 90.9 92.8* 3.35 100.0 98.3 - - - - - - Mean 99.1 94.1 95.4 91.0 C.V. 1.1% 1.0% 3.2% 1.8% 1.0M Hcl
µl per CanSTORAGE CONDITION/1.0% isopropyl myristate Initial 40°C; 33days 50°C; 11 days 50°C; 31 days 1st Can 2nd Can 1st Can 2nd Can 1st Can 2nd Can 1st Can 2nd Can 3.15 101.1 99.3 - - - - - - 3.20 97.0 100.2 94.4 93.2* 93.8 93.6 90.6 92.7* 3.25 101.4 100.2 98.6 95.0* 96.1 95.9 91.6 89.7* 3.30 99.9 100.8 92.8 95.3* 95.6 95.7 90.0 89.6* 3.35 99.2 97.2 - - - - - - Mean 99.6 94.9 95.1 90.7 C.V. 1.5% 2.2% 1.2% 1.4% Table 6: Shelf Life Prediction for Acidified Formoterol Fumarate Solution (12µg/100µl) in HFA 134a containing 12% w/w Ethanol ± 1.0% w/w isopropyl Myristate (IPM) Anodised aluminium cans TIME
(days)FORMOTEROL FUMARATE (percent nominal) 40° C Nil IPM 1% IPM Nil IPM 1 % IPM 0 99.1 99.6 99.1 99.6 11 95.4 95.1 - - 31 - 90.7 - - 33 91.0 - - 94.9 40 - - 94.1 - Rate Const.
(day-1 x 103)2.52 2.94 1.29 1.46 Arrhenius Parameters Frequency Activation Factor (day-1) Energy (kJ mol-1) Nil IPM 3.19 x106 56.3 1% w/w IPM 9.63x106 58.9 TEMPERATURE Nil IPM 1.0% w/w IPM Rate Const. t10% t5% Rate Const. t10% t5%, (day-1) (days) (day-1) (days) 4°C 7.8x10-5 1344 657 7.8x10-5 1360 664 10°C 1.3x10-4 802 392 1.3x10-4 789 386 25°C 4.4x10-4 240 117 4.4x10-4 225 110 - Formoterol and BDP combination formulations equivalent to doses of 6 µg/50 µl and 100 µg/50 µl respectively, were prepared by dissolving 1.44 mg of formoterol fumarate and 24 mg of BDP in HFA 134a containing 12% w/w ethanol and 0.4% w/w of isopropyl myristate. pMDI coated cans containing 3.25 µl 1.0 M hydrochloric acid were set down on storage inverted, at 4°C and samples taken for analysis of formoterol and BDP contents at appropriate intervals.
- Stability data obtained are given in Table 7.
- Each value is expressed as per cent nominal drug concentration.
- The results indicate that the formulation is stable for at least 4 months at 4° C.
Table 7: Formoterol/BDP combination formulations of Ex 6 - Stability data at 4°C Storage Condition Initial 4°C; 64 days
inverted4°C; 123 days
invertedFormoterol 104.7 95.10 99.9 BDP 99.4 100.10 102.6
Claims (4)
- An aerosol composition which comprises as active ingredient formoterol fumarate in a solution of a liquefied HFA 134a propellant and ethanol as a co-solvent, and hydrochloric acid in an amount such that the solution has an apparent pH between 3.0 and 3.5.
- An aerosol composition according to claim 1 which comprises as active ingredient formoterol fumarate in a solution of a liquefied HFA 134a propellant and ethanol as a co-solvent, and 1.0 M hydrochloric acid in an amount between 3 and 3.5 µl per 1.44 mg formoterol fumarate in 12 mL of the composition.
- A composition according to any one of claim 1 or 2, which is filled in a container having part or all of its internal metallic surfaces made of stainless steel, anodised aluminium or lined with an inert organic coating.
- A composition according to claim 3, wherein said container is lined with an inert organic coating selected from epoxy-phenol resins, perfluoroalkoxyalkane, perfluoroalkoxyalkylene, perfluoroalkylenes such as polytetrafluoroethylene, fluorinated-ethylene-propylene, polyether sulfone and a copolymer fluorinated-ethylene-propylene polyether sulfone.
Priority Applications (14)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP07004772A EP1787639B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| SI200130907T SI1157689T1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP04011423A EP1466594B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP01112230A EP1157689B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP10166800A EP2223682B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| DK07004772.5T DK1787639T3 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical formulations for pressure dose inhalers |
| NO20025568A NO342935B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2002-11-20 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for use in metered dose inhalers |
| CY20091100391T CY1108968T1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2009-04-03 | STABLE PHARMACEUTICAL PHARMACEUTICAL SOLUTIONS FOR SOLID PRESSURE INHIBITION DEVICES |
| CY2009009C CY2009009I1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2009-07-03 | STABLE PHARMACEUTICAL PHARMACEUTICAL SOLUTION FORMS FOR PRESSURE METERED DOSE INHALATION DEVICES |
| LTPA2011011C LTC1787639I2 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2011-09-20 | Stable pharmaceutical solution preparations for pressure metered dose inhalers |
| BE2011C032C BE2011C032I2 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2011-09-20 | |
| CY2011014C CY2011014I1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2011-09-22 | PHARMACEUTICAL FORMS OF STABLE PHARMACEUTICAL SOLUTION FOR PRESSURE METERED DOSE INHALATION DEVICES |
| FR11C0041C FR11C0041I2 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2011-09-23 | FORMULATIONS OF STABLE PHARMACEUTICAL SOLUTIONS FOR PRESSURIZED MEASUREMENT INHALERS |
| NO2019003C NO2019003I1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2019-01-16 | Combination of formoterol fumarate dihydrate and beclomethasone dipropionate |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOPCT/EP00/04635 | 2000-05-22 | ||
| PCT/EP2000/004635 WO2001089480A1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2000-05-22 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP01112230A EP1157689B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04011423A Division EP1466594B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP07004772A Division EP1787639B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1157689A1 EP1157689A1 (en) | 2001-11-28 |
| EP1157689B1 true EP1157689B1 (en) | 2009-01-07 |
Family
ID=8163952
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP01112230A Revoked EP1157689B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP04011423A Expired - Lifetime EP1466594B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP07004772A Expired - Lifetime EP1787639B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP10166800A Expired - Lifetime EP2223682B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
Family Applications After (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04011423A Expired - Lifetime EP1466594B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP07004772A Expired - Lifetime EP1787639B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP10166800A Expired - Lifetime EP2223682B1 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2001-05-18 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
Country Status (41)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US6716414B2 (en) |
| EP (4) | EP1157689B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5392880B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1213732C (en) |
| AR (1) | AR029523A1 (en) |
| AT (4) | ATE502624T1 (en) |
| AU (2) | AU5070100A (en) |
| BE (1) | BE2011C032I2 (en) |
| BG (1) | BG65883B1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR0015884A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2411047C (en) |
| CY (6) | CY1108833T1 (en) |
| CZ (1) | CZ303833B6 (en) |
| DE (5) | DE60144304D1 (en) |
| DK (4) | DK1787639T3 (en) |
| DZ (1) | DZ3358A1 (en) |
| EA (1) | EA005179B1 (en) |
| EE (1) | EE05167B1 (en) |
| ES (4) | ES2359991T3 (en) |
| FR (1) | FR11C0041I2 (en) |
| HK (1) | HK1058900A1 (en) |
| HR (1) | HRP20021025B1 (en) |
| HU (2) | HU230804B1 (en) |
| IL (2) | IL152955A0 (en) |
| JO (1) | JO2310B1 (en) |
| LT (1) | LTC1787639I2 (en) |
| LU (1) | LU91875I2 (en) |
| ME (2) | ME00220B (en) |
| MX (1) | MXPA02011414A (en) |
| MY (2) | MY127145A (en) |
| NL (1) | NL300393I2 (en) |
| NO (3) | NO342935B1 (en) |
| PE (1) | PE20011323A1 (en) |
| PT (4) | PT1466594E (en) |
| SA (1) | SA01220126B1 (en) |
| SI (4) | SI1787639T1 (en) |
| SK (1) | SK286694B6 (en) |
| TN (1) | TNSN01074A1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI284047B (en) |
| UA (1) | UA73986C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2001089480A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007500676A (en) * | 2003-07-31 | 2007-01-18 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Inhalable drugs including anticholinergics and beta receptor stimulants |
| EP2010190A2 (en) | 2006-04-21 | 2009-01-07 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| US8114912B2 (en) | 2003-07-10 | 2012-02-14 | Mylan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Bronchodilating β-agonist compositions and methods |
Families Citing this family (103)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20010031244A1 (en) * | 1997-06-13 | 2001-10-18 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | Pharmaceutical aerosol composition |
| DZ2947A1 (en) * | 1998-11-25 | 2004-03-15 | Chiesi Farma Spa | Pressure metered dose inhaler. |
| IT1303788B1 (en) * | 1998-11-25 | 2001-02-23 | Chiesi Farma Spa | MEDICINAL AEROSOL FORMULATIONS. |
| US6315985B1 (en) * | 1999-06-18 | 2001-11-13 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | C-17/21 OH 20-ketosteroid solution aerosol products with enhanced chemical stability |
| ES2165768B1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2003-04-01 | Almirall Prodesfarma Sa | NEW DERIVATIVES OF QUINUCLIDINE AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS THAT CONTAIN THEM. |
| IT1313553B1 (en) | 1999-07-23 | 2002-09-09 | Chiesi Farma Spa | OPTIMIZED FORMULATIONS CONSTITUTED BY SOLUTIONS OF STEROIDS GIVEN BY INHALATION. |
| DE60017450T2 (en) * | 1999-11-23 | 2006-03-02 | Glaxo Group Ltd., Greenford | PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATIONS CONTAINING SALMETEROL |
| IT1317720B1 (en) * | 2000-01-07 | 2003-07-15 | Chiesi Farma Spa | DEVICE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF AEROSOL DOSED PRESSURIZED INPROPELLENT HYDROFLUOROALKANS. |
| IT1318514B1 (en) * | 2000-05-12 | 2003-08-27 | Chiesi Farma Spa | FORMULATIONS CONTAINING A GLUCOCORTICOSTEROID DRUG FOR THE TREATMENT OF BRONCOPOLMONARY DISEASES. |
| ME00220B (en) * | 2000-05-22 | 2010-10-10 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| KR100849582B1 (en) * | 2000-05-23 | 2008-07-31 | 글락소 그룹 리미티드 | Aerosol container for formulations of salmeterol xinafoate |
| FI20002177A0 (en) * | 2000-10-02 | 2000-10-02 | Orion Yhtymae Oyj | New combination for asthma therapy |
| EP1241113A1 (en) | 2001-03-12 | 2002-09-18 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Inhaler with means for improving chemical stability of medicinal aerosol solution contained therein |
| RU2294737C2 (en) * | 2001-03-30 | 2007-03-10 | Яготек Аг | Medicinal aerosol compositions |
| US20030055026A1 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2003-03-20 | Dey L.P. | Formoterol/steroid bronchodilating compositions and methods of use thereof |
| US6667344B2 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2003-12-23 | Dey, L.P. | Bronchodilating compositions and methods |
| DK1273292T3 (en) | 2001-07-02 | 2004-10-04 | Chiesi Farma Spa | Optimized tobramycin formulation for aerosol formation |
| US7906102B2 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2011-03-15 | Vanderbilt University | Ligands to radiation-induced molecules |
| US7306925B2 (en) | 2001-11-09 | 2007-12-11 | Vanderbilt University | Phage antibodies to radiation-inducible neoantigens |
| HUE049426T2 (en) * | 2002-03-01 | 2020-09-28 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Formoterol superfine formulation |
| EP1415647A1 (en) * | 2002-10-23 | 2004-05-06 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | "Long-acting beta-2 agonists ultrafine formulations" |
| EP1340492A1 (en) * | 2002-03-01 | 2003-09-03 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Aerosol formulations for pulmonary administration of medicaments having systemic effects |
| JP4602767B2 (en) * | 2002-08-14 | 2010-12-22 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム ファルマ ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング ウント コンパニー コマンディトゲゼルシャフト | Aerosol formulation for inhalation containing anticholinergics |
| US20040166065A1 (en) | 2002-08-14 | 2004-08-26 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Gmbh & Co. Kg | Aerosol formulation for inhalation comprising an anticholinergic |
| US7244742B2 (en) * | 2002-08-17 | 2007-07-17 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Gmbh & Co Kg | Pharmaceutical compositions for inhalation containing an anticholinergic, corticosteroid and betamimetic |
| EP1452179A1 (en) * | 2003-02-27 | 2004-09-01 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Novel medicament combination of a highly potent long-lasting beta2-agonist and a corticosteroid |
| US20050003024A1 (en) * | 2003-03-04 | 2005-01-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Regulation of mammalian hair growth |
| US20050026948A1 (en) * | 2003-07-29 | 2005-02-03 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Medicaments for inhalation comprising an anticholinergic and a betamimetic |
| JP2007501194A (en) * | 2003-08-05 | 2007-01-25 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Inhalable drugs including steroids and beta mimetics |
| AU2004271779A1 (en) * | 2003-09-15 | 2005-03-24 | Vectura Limited | Pharmaceutical compositions for treating premature ejaculation by pulmonary inhalation |
| GB0323684D0 (en) | 2003-10-09 | 2003-11-12 | Jagotec Ag | Improvements in or relating to organic compounds |
| AR041873A1 (en) * | 2003-10-30 | 2005-06-01 | Pablo Cassara Srl Lab | A PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION IN ADEQUATE AEROSOL FOR ORAL OR NASAL INHALATION CONTAINING GLUCOCORTICOIDS IN A STABLE SOLUTION TO STORAGE; A METHOD FOR STABILIZING FORMULATIONS AND USE OF A STABILIZING AGENT |
| KR20070000476A (en) * | 2004-02-27 | 2007-01-02 | 키에시 파르마슈티시 엣스. 피. 에이. | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
| CN100457087C (en) * | 2004-02-27 | 2009-02-04 | 奇斯药制品公司 | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulation for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
| EP1595531A1 (en) * | 2004-05-13 | 2005-11-16 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
| JP2007537170A (en) * | 2004-05-13 | 2007-12-20 | チエシイ・ファルマセウテイシイ・エス・ペー・アー | Medicinal aerosol formulation products with improved chemical stability |
| ES2257152B1 (en) * | 2004-05-31 | 2007-07-01 | Laboratorios Almirall S.A. | COMBINATIONS THAT INCLUDE ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS AND BETA-ADRENERGIC AGONISTS. |
| GB0501956D0 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2005-03-09 | Arrow Internat | Nebulizer formulation |
| GEP20105040B (en) | 2005-02-25 | 2010-07-12 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers comprising a sequestering agent |
| JP2008534611A (en) * | 2005-03-30 | 2008-08-28 | シェーリング コーポレイション | Drugs and methods combining anticholinergics, corticosteroids and long acting beta agonists |
| DE102005055960A1 (en) * | 2005-11-24 | 2007-07-19 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Gmbh & Co. Kg | Aerosol formulation for inhalation containing an anticholinergic |
| GB0525680D0 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2006-01-25 | Peplin Ltd | Therapeutic compositions |
| US20070286814A1 (en) * | 2006-06-12 | 2007-12-13 | Medispray Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | Stable aerosol pharmaceutical formulations |
| GB0613761D0 (en) * | 2006-07-11 | 2006-08-23 | Norton Healthcare Ltd | A pharmaceutical formulation and method for the preparation thereof |
| EP1982709A1 (en) | 2007-04-19 | 2008-10-22 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Use of a composition comprising formoterol and beclomethasone dipropionate for the prevention or treatment of an acute condition of asthma |
| US8227027B2 (en) | 2007-12-07 | 2012-07-24 | Presspart Gmbh & Co. Kg | Method for applying a polymer coating to an internal surface of a container |
| EP2077132A1 (en) | 2008-01-02 | 2009-07-08 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG | Dispensing device, storage device and method for dispensing a formulation |
| GB0801876D0 (en) * | 2008-02-01 | 2008-03-12 | Vectura Group Plc | Suspension formulations |
| US20090208424A1 (en) * | 2008-02-19 | 2009-08-20 | Todd Maibach | Compositions and methods for delivery of solution to the skin |
| US20100055045A1 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2010-03-04 | William Gerhart | Method and system for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with nebulized anticholinergic administrations |
| GB2468073B (en) * | 2008-02-26 | 2012-09-05 | Elevation Pharmaceuticals Inc | Method and system for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with nebulized anticholinergic administrations |
| EP2100598A1 (en) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-16 | Laboratorios Almirall, S.A. | Inhalation composition containing aclidinium for treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| EP2100599A1 (en) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-16 | Laboratorios Almirall, S.A. | Inhalation composition containing aclidinium for treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| JP2012506860A (en) * | 2008-10-23 | 2012-03-22 | サノビオン ファーマシューティカルズ インク | Composition of alformoterol and tiotropium and methods of use thereof |
| EP2201934A1 (en) * | 2008-12-23 | 2010-06-30 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Tiotropium aerosol formulation products with improved chemical stability |
| EP2662472B1 (en) | 2009-03-31 | 2019-02-27 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Method for coating a surface of a component |
| US9265910B2 (en) | 2009-05-18 | 2016-02-23 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Adapter, inhalation device, and nebulizer |
| HUE029159T2 (en) * | 2009-10-02 | 2017-02-28 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulations of formoterol and beclometasone dipropionate |
| GB0918150D0 (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2009-12-02 | Jagotec Ag | Improved formulations |
| GB0918149D0 (en) | 2009-10-16 | 2009-12-02 | Jagotec Ag | Improved medicinal aerosol formulation |
| PE20130036A1 (en) | 2009-11-25 | 2013-02-03 | Boehringer Ingelheim Int | Nebulizer |
| US10016568B2 (en) | 2009-11-25 | 2018-07-10 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Nebulizer |
| EP2504051B1 (en) | 2009-11-25 | 2019-09-04 | Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH | Nebulizer |
| EP2512438B1 (en) | 2009-12-16 | 2017-01-25 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Formulations and methods for controlling mdi particle size delivery |
| KR101738712B1 (en) * | 2009-12-23 | 2017-05-22 | 키에시 파르마슈티시 엣스. 피. 에이. | Combination therapy for copd |
| EA021917B1 (en) * | 2009-12-23 | 2015-09-30 | КЬЕЗИ ФАРМАЧЕУТИЧИ С.п.А. | Combination therapy for asthma and copd |
| EA021604B1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2015-07-30 | КЬЕЗИ ФАРМАЧЕУТИЧИ С.п.А. | Aerosol formulation for treating asthma and copd |
| JP5874724B2 (en) | 2010-06-24 | 2016-03-02 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Nebulizer |
| WO2012010854A1 (en) | 2010-07-23 | 2012-01-26 | Cipla Limited | Inhalation formulations comprising carmoterol in combination with a corticosteroid |
| EP2694220B1 (en) | 2011-04-01 | 2020-05-06 | Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH | Medical device comprising a container |
| EP2510928A1 (en) | 2011-04-15 | 2012-10-17 | Almirall, S.A. | Aclidinium for use in improving the quality of sleep in respiratory patients |
| US9827384B2 (en) | 2011-05-23 | 2017-11-28 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Nebulizer |
| WO2013019730A1 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2013-02-07 | The Washington University | Antibodies to tip-1 and grp78 |
| GB201200525D0 (en) | 2011-12-19 | 2012-02-29 | Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Prod R & D Inc | An inhalable medicament |
| GB201200504D0 (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2012-02-22 | Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Prod R & D Inc | An inhaler |
| WO2013152894A1 (en) | 2012-04-13 | 2013-10-17 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Atomiser with coding means |
| PL2835146T3 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2021-04-06 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Nebulizer |
| EP3030298B1 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2017-10-11 | Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH | Nebulizer |
| MY176191A (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2020-07-24 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Stable pressurised aerosol solution composition of glycopyrronium bromide and formoterol combination |
| AU2014375301B2 (en) | 2013-12-30 | 2020-03-26 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | Stable pressurised aerosol solution composition of glycopyrronium bromide and formoterol combination |
| EP3139984B1 (en) | 2014-05-07 | 2021-04-28 | Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH | Nebulizer |
| ES2957901T3 (en) | 2014-05-07 | 2024-01-29 | Boehringer Ingelheim Int | Container and indicator device and nebulizer |
| WO2015169732A1 (en) | 2014-05-07 | 2015-11-12 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Container, nebulizer and use |
| US10034866B2 (en) | 2014-06-19 | 2018-07-31 | Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Products R&D, Inc. | Inhalable medicament comprising tiotropium |
| US10449261B2 (en) | 2014-07-24 | 2019-10-22 | Washington University | Compositions targeting radiation-induced molecules and methods of use thereof |
| CN104225739A (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2014-12-24 | 四川普锐特医药科技有限责任公司 | Medical quantitative inhalation aerosol |
| MX2018006800A (en) | 2015-12-04 | 2018-11-09 | Mexichem Fluor Sa De Cv | Pharmaceutical composition. |
| US10098837B2 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2018-10-16 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | Combination therapy for COPD |
| US11352436B2 (en) | 2017-02-10 | 2022-06-07 | Washington University | Antibodies to TIP1 and methods of use thereof |
| JOP20200314A1 (en) | 2018-06-04 | 2020-12-06 | Lupin Inc | Stable pharmaceutical compositions for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
| WO2020152548A1 (en) * | 2019-01-24 | 2020-07-30 | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Limited | Stable aerosol inhalation compositions of formoterol |
| CN112137957B (en) | 2019-06-26 | 2022-07-29 | 长风药业股份有限公司 | Medicinal inhalation aerosol and preparation method thereof |
| PE20221439A1 (en) * | 2019-12-02 | 2022-09-21 | Chiesi Farm Spa | STAINLESS STEEL CAN FOR PRESSURIZED MDI INHALERS |
| IL294804A (en) | 2020-01-28 | 2022-09-01 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Pressurised metered dose inhalers comprising a buffered pharmaceutical formulation |
| GB2593970A (en) | 2020-02-20 | 2021-10-13 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Pressurised metered dose inhalers comprising a buffered pharmaceutical formulation |
| US11826382B2 (en) | 2020-05-01 | 2023-11-28 | Tygrus, LLC | Therapeutic material with low pH and low toxicity active against at least one pathogen for addressing patients with respiratory illnesses |
| US11642372B2 (en) * | 2020-05-01 | 2023-05-09 | Tygrus, LLC | Therapeutic material with low pH and low toxicity active against at least one pathogen for addressing patients with respiratory illnesses |
| KR20230052903A (en) | 2020-07-31 | 2023-04-20 | 케모 리서치, 에스.엘. | Combination therapy for administration by inhalation |
| KR20230084482A (en) * | 2020-10-09 | 2023-06-13 | 키에시 파르마슈티시 엣스. 피. 에이. | Pharmaceutical formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
| GB2614901A (en) | 2022-01-21 | 2023-07-26 | Nanopharm Ltd | Inhalable formulations |
| US20230322741A1 (en) | 2022-04-06 | 2023-10-12 | Rapt Therapeutics, Inc. | Chemokine receptor modulators and uses thereof |
| WO2023227782A1 (en) | 2022-05-27 | 2023-11-30 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | A pharmaceutical formulation for pressurised metered dose inhaler |
| WO2023227783A1 (en) | 2022-05-27 | 2023-11-30 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | A pharmaceutical formulation for pressurised metered dose inhaler |
Family Cites Families (80)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3361306A (en) | 1966-03-31 | 1968-01-02 | Merck & Co Inc | Aerosol unit dispensing uniform amounts of a medically active ingredient |
| US3622053A (en) | 1969-12-10 | 1971-11-23 | Schering Corp | Aerosol inhaler with flip-up nozzle |
| MX3864E (en) | 1975-05-27 | 1981-08-26 | Syntex Corp | A PROCESS TO PREPARE THE CRYSTALLINE COMPOUND 6-FLUIRO-11B 21-DIHIROXI-16 17-ISOPROPILIDENDIOXIPREGNA-1 4-DIEN-3 20-DIONA |
| US4185100A (en) | 1976-05-13 | 1980-01-22 | Johnson & Johnson | Topical anti-inflammatory drug therapy |
| US4499108A (en) * | 1983-06-08 | 1985-02-12 | Schering Corporation | Stable pleasant-tasting albuterol sulfate pharmaceutical formulations |
| GB8334494D0 (en) * | 1983-12-24 | 1984-02-01 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co | Carbostyril derivatives |
| IT1196142B (en) | 1984-06-11 | 1988-11-10 | Sicor Spa | PROCEDURE FOR THE PREPARATION OF 16.17-ACETALS OF PREGNANIC DERIVATIVES AND NEW COMPOUNDS OBTAINED |
| US5192528A (en) | 1985-05-22 | 1993-03-09 | Liposome Technology, Inc. | Corticosteroid inhalation treatment method |
| US5225183A (en) | 1988-12-06 | 1993-07-06 | Riker Laboratories, Inc. | Medicinal aerosol formulations |
| GB8828477D0 (en) * | 1988-12-06 | 1989-01-05 | Riker Laboratories Inc | Medical aerosol formulations |
| IL97065A (en) | 1990-02-02 | 1994-01-25 | Fisons Plc | Aerosol propellant compositions |
| WO1992011236A1 (en) | 1990-12-19 | 1992-07-09 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | Aerosol formulations |
| US6006745A (en) | 1990-12-21 | 1999-12-28 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Device for delivering an aerosol |
| EP0504112A3 (en) | 1991-03-14 | 1993-04-21 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulations |
| US5874063A (en) * | 1991-04-11 | 1999-02-23 | Astra Aktiebolag | Pharmaceutical formulation |
| RU2114642C1 (en) | 1991-05-21 | 1998-07-10 | Эбботт Лабораториз | Aerosol inhalation device |
| AU653634B2 (en) | 1991-08-29 | 1994-10-06 | Broncho-Air Medizintechnik Ag | Medical appliance for inhaling metered aerosols |
| NZ244439A (en) | 1991-09-25 | 1994-01-26 | Fisons Plc | Pressurised aerosol compositions comprising hydrofluoroalkane, dispersed |
| IL104068A (en) | 1991-12-12 | 1998-10-30 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Surfactant-free pharmaceutical aerosol formulation comprising 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane or 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoro-n- propane as propellant |
| EP0617610B1 (en) | 1991-12-18 | 1997-03-19 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Suspension aerosol formulations |
| DE4230876A1 (en) | 1992-03-17 | 1993-09-23 | Asta Medica Ag | COMPRESSED GAS PACKS USING POLYOXYETHYLENE GLYCERYL OLEATES |
| UA27143C2 (en) * | 1992-12-09 | 2000-02-28 | Берінгер Інгельхейм Фармасьютікалс Інк | Liquid pharmaceutical composition as an aerosol |
| SE9203743D0 (en) * | 1992-12-11 | 1992-12-11 | Astra Ab | EFFICIENT USE |
| WO1994014490A1 (en) | 1992-12-23 | 1994-07-07 | Bernhard Hugemann | Compacted drug body for use in the mechanical generation of inhalable active-substance particles |
| NZ263686A (en) * | 1993-03-17 | 1997-09-22 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Medicinal aerosol with dispersing aid derived from a hydroxy acid, an amino acid and/or a mercapto acid |
| AU679510B2 (en) * | 1993-03-17 | 1997-07-03 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Aerosol formulation containing a diol-diacid derived dispersing aid |
| US6596260B1 (en) | 1993-08-27 | 2003-07-22 | Novartis Corporation | Aerosol container and a method for storage and administration of a predetermined amount of a pharmaceutically active aerosol |
| DE69424181T2 (en) | 1993-12-20 | 2000-10-19 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | FLUNISOLIDE AEROSOL FORMULATIONS |
| GB9425160D0 (en) | 1994-12-10 | 1995-02-08 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Medicaments |
| MX9704550A (en) * | 1994-12-22 | 1997-10-31 | Astra Ab | Aerosol drug formulations. |
| GB9426252D0 (en) * | 1994-12-24 | 1995-02-22 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Pharmaceutical composition |
| DE4446891A1 (en) | 1994-12-27 | 1996-07-04 | Falk Pharma Gmbh | Stable aqueous budesonide solution |
| US5653961A (en) | 1995-03-31 | 1997-08-05 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Butixocort aerosol formulations in hydrofluorocarbon propellant |
| EP1908488A3 (en) | 1995-04-14 | 2008-04-16 | SmithKline Beecham Corporation | Metered dose inhaler for salmeterol |
| DE69636757T2 (en) | 1995-04-14 | 2007-10-11 | Smithkline Beecham Corp. | Dosing inhaler for fluticasone propionate |
| PL180880B1 (en) | 1995-04-14 | 2001-04-30 | Glaxo Wellcome Inc | Beclomethasone inhaler with dosis metering feature |
| EP1870122A3 (en) | 1995-04-14 | 2008-03-12 | SmithKline Beecham Corporation | Metered dose inhaler |
| US6135628A (en) * | 1995-10-13 | 2000-10-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmceuticals, Inc. | Method and apparatus for homogenizing aerosol formulations |
| GB9612297D0 (en) | 1996-06-11 | 1996-08-14 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Medicinal aerosol formulations |
| AU3453897A (en) | 1996-07-08 | 1998-02-02 | Rhone-Poulenc Rorer Limited | Medicinal cyclosporin-a aerosol solution formulation |
| AU3811897A (en) | 1996-07-24 | 1998-02-10 | Oglios Therapeutics, Inc. | Antisense oligonucleotides as antibacterial agents |
| GB9616237D0 (en) | 1996-08-01 | 1996-09-11 | Norton Healthcare Ltd | Aerosol formulations |
| GB9620187D0 (en) | 1996-09-27 | 1996-11-13 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Medicinal aerosol formulations |
| US6413496B1 (en) | 1996-12-04 | 2002-07-02 | Biogland Ireland (R&D) Limited | Pharmaceutical compositions and devices for their administration |
| CA2273835A1 (en) * | 1996-12-04 | 1998-06-11 | Bioglan Ireland (R & D) Limited | Pharmaceutical compositions and devices for their administration |
| DK1014943T3 (en) | 1997-02-05 | 2002-10-14 | Jago Res Ag | Medical aerosol formulations |
| US6126919A (en) | 1997-02-07 | 2000-10-03 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Biocompatible compounds for pharmaceutical drug delivery systems |
| US5891419A (en) | 1997-04-21 | 1999-04-06 | Aeropharm Technology Limited | Environmentally safe flunisolide aerosol formulations for oral inhalation |
| US6000537A (en) * | 1997-06-10 | 1999-12-14 | U.S. Philips Corporation | Housing with readable side walls for a disc-shaped information carrier |
| GB2326334A (en) | 1997-06-13 | 1998-12-23 | Chiesi Farma Spa | Pharmaceutical aerosol compositions |
| US20010031244A1 (en) * | 1997-06-13 | 2001-10-18 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | Pharmaceutical aerosol composition |
| US6324827B1 (en) * | 1997-07-01 | 2001-12-04 | Bp Corporation North America Inc. | Method of generating power in a dry low NOx combustion system |
| BR7702049U (en) | 1997-09-05 | 1999-09-14 | Chiesi Farma Spa | Spray nozzle for use in an oral inhaler for aerosol medicines |
| US5954047A (en) | 1997-10-17 | 1999-09-21 | Systemic Pulmonary Development, Ltd. | Methods and apparatus for delivering aerosolized medication |
| AU2081999A (en) * | 1998-01-13 | 1999-08-02 | Astrazeneca Uk Limited | Pharmaceutical compostition comprising a compound having dopamine (D2) receptor agonist activity and a compound (B) having Beta2 adrenoreceptor agonist activity |
| US6045784A (en) | 1998-05-07 | 2000-04-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Aerosol package compositions containing fluorinated hydrocarbon propellants |
| SE9802073D0 (en) | 1998-06-11 | 1998-06-11 | Astra Ab | New use |
| SK284756B6 (en) * | 1998-06-18 | 2005-11-03 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutical preparation for propellant driven metered dose inhalers, where the propellant is fluorohydrocarbon, containing a combination of two or more active substances |
| US6451285B2 (en) | 1998-06-19 | 2002-09-17 | Baker Norton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Suspension aerosol formulations containing formoterol fumarate and a fluoroalkane propellant |
| US6241969B1 (en) | 1998-06-26 | 2001-06-05 | Elan Corporation Plc | Aqueous compositions containing corticosteroids for nasal and pulmonary delivery |
| WO2000006121A1 (en) * | 1998-07-24 | 2000-02-10 | Jago Research Ag | Medicinal aerosol formulations |
| ES2193726T3 (en) * | 1998-08-04 | 2003-11-01 | Jago Res Ag | MEDICINAL AEROSOL FORMULATIONS. |
| US6136294C1 (en) * | 1998-09-22 | 2002-09-24 | Aeropharm Technology Inc | Amino acid stabilized medical aerosol formulation |
| DE19847969A1 (en) | 1998-10-17 | 2000-04-20 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma | Stable liquid formulation of formoterol in solution or suspension medium, used after dilution for treatment of asthma by inhalation |
| ID29605A (en) * | 1998-10-17 | 2001-09-06 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma | CONCENTRATES OF ACTIVE MATERIALS WITH FORMOTEROLS, WHICH ARE ACCORDING TO STORAGE |
| CZ303154B6 (en) | 1998-11-13 | 2012-05-09 | Jagotec Ag | Dry powder formulation for inhalation containing magnesium stearate |
| DZ2947A1 (en) * | 1998-11-25 | 2004-03-15 | Chiesi Farma Spa | Pressure metered dose inhaler. |
| IT1303788B1 (en) * | 1998-11-25 | 2001-02-23 | Chiesi Farma Spa | MEDICINAL AEROSOL FORMULATIONS. |
| US6290930B1 (en) | 1998-12-18 | 2001-09-18 | Baker Norton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutical solution aerosol formulations containing fluoroalkanes and budesonide |
| US6004537A (en) * | 1998-12-18 | 1999-12-21 | Baker Norton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutical solution aerosol formulations containing fluoroalkanes, budesonide and formoterol |
| GB9902689D0 (en) * | 1999-02-08 | 1999-03-31 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| DE69936268T2 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2008-02-14 | Chiesi Farmaceutici S.P.A. | Improved powdered pharmaceutical compositions for use in dry powder inhalers |
| US6315985B1 (en) | 1999-06-18 | 2001-11-13 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | C-17/21 OH 20-ketosteroid solution aerosol products with enhanced chemical stability |
| EP1248597B1 (en) | 1999-12-24 | 2005-03-30 | Glaxo Group Limited | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulation of salmeterol and fluticasone propionate |
| IT1317846B1 (en) | 2000-02-22 | 2003-07-15 | Chiesi Farma Spa | FORMULATIONS CONTAINING AN ANTICOLINERGIC DRUG FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE BRONCOPNEUMOPATHY. |
| IT1318514B1 (en) | 2000-05-12 | 2003-08-27 | Chiesi Farma Spa | FORMULATIONS CONTAINING A GLUCOCORTICOSTEROID DRUG FOR THE TREATMENT OF BRONCOPOLMONARY DISEASES. |
| ME00220B (en) * | 2000-05-22 | 2010-10-10 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
| EP1340492A1 (en) * | 2002-03-01 | 2003-09-03 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Aerosol formulations for pulmonary administration of medicaments having systemic effects |
| HUE049426T2 (en) * | 2002-03-01 | 2020-09-28 | Chiesi Farm Spa | Formoterol superfine formulation |
| EP1595531A1 (en) * | 2004-05-13 | 2005-11-16 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
-
2000
- 2000-05-22 ME MEP-2008-321A patent/ME00220B/en unknown
- 2000-05-22 EE EEP200200649A patent/EE05167B1/en unknown
- 2000-05-22 HU HU0302007A patent/HU230804B1/en active Protection Beyond IP Right Term
- 2000-05-22 MX MXPA02011414A patent/MXPA02011414A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2000-05-22 EA EA200201058A patent/EA005179B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-22 AU AU5070100A patent/AU5070100A/en active Pending
- 2000-05-22 DZ DZ003358A patent/DZ3358A1/en active
- 2000-05-22 IL IL15295500A patent/IL152955A0/en unknown
- 2000-05-22 UA UA2002118859A patent/UA73986C2/en unknown
- 2000-05-22 AU AU2000250701A patent/AU2000250701B2/en not_active Expired
- 2000-05-22 CA CA002411047A patent/CA2411047C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-22 SK SK1652-2002A patent/SK286694B6/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-22 BR BR0015884-4A patent/BR0015884A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-22 CN CNB008195641A patent/CN1213732C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-22 WO PCT/EP2000/004635 patent/WO2001089480A1/en active Application Filing
- 2000-05-22 JP JP2001585725A patent/JP5392880B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-22 CZ CZ20023835A patent/CZ303833B6/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2001
- 2001-05-17 PE PE2001000439A patent/PE20011323A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2001-05-17 JO JO200172A patent/JO2310B1/en active
- 2001-05-18 PT PT04011423T patent/PT1466594E/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 DE DE60144304T patent/DE60144304D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 ES ES07004772T patent/ES2359991T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 AT AT07004772T patent/ATE502624T1/en active
- 2001-05-18 PT PT10166800T patent/PT2223682E/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 EP EP01112230A patent/EP1157689B1/en not_active Revoked
- 2001-05-18 SI SI200130992T patent/SI1787639T1/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 DE DE60136864T patent/DE60136864D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 DK DK07004772.5T patent/DK1787639T3/en active
- 2001-05-18 PT PT01112230T patent/PT1157689E/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 ES ES10166800T patent/ES2380790T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 DE DE60137282T patent/DE60137282D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 ES ES04011423T patent/ES2318217T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 DK DK01112230T patent/DK1157689T3/en active
- 2001-05-18 SI SI200131010T patent/SI2223682T1/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 AT AT01112230T patent/ATE419832T1/en active
- 2001-05-18 EP EP04011423A patent/EP1466594B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 DE DE122009000035C patent/DE122009000035I1/en active Pending
- 2001-05-18 MY MYPI20012370 patent/MY127145A/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 SI SI200130907T patent/SI1157689T1/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 ES ES01112230T patent/ES2320194T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 MY MYPI20060219A patent/MY143733A/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 AT AT10166800T patent/ATE541563T1/en active
- 2001-05-18 DK DK10166800.2T patent/DK2223682T3/en active
- 2001-05-18 SI SI200130902T patent/SI1466594T1/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 AT AT04011423T patent/ATE415945T1/en active
- 2001-05-18 PT PT07004772T patent/PT1787639E/en unknown
- 2001-05-18 DK DK04011423T patent/DK1466594T3/en active
- 2001-05-18 EP EP07004772A patent/EP1787639B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-18 EP EP10166800A patent/EP2223682B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-21 SA SA01220126A patent/SA01220126B1/en unknown
- 2001-05-21 AR ARP010102397A patent/AR029523A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2001-05-21 US US09/860,689 patent/US6716414B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-05-22 TW TW090112202A patent/TWI284047B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-05-22 TN TNTNSN01074A patent/TNSN01074A1/en unknown
-
2002
- 2002-11-08 BG BG107256A patent/BG65883B1/en unknown
- 2002-11-20 NO NO20025568A patent/NO342935B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-11-20 IL IL152955A patent/IL152955A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-12-20 HR HRP20021025AA patent/HRP20021025B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2003
- 2003-08-14 US US10/640,005 patent/US7018618B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2004
- 2004-03-12 HK HK04101816A patent/HK1058900A1/en unknown
-
2005
- 2005-05-22 ME MEP-321/08A patent/MEP32108A/en unknown
- 2005-11-30 US US11/289,479 patent/US20060083693A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2009
- 2009-02-27 CY CY20091100233T patent/CY1108833T1/en unknown
- 2009-04-03 CY CY20091100391T patent/CY1108968T1/en unknown
- 2009-07-03 NL NL300393C patent/NL300393I2/en unknown
- 2009-07-03 CY CY2009009C patent/CY2009009I1/en unknown
-
2011
- 2011-06-20 CY CY20111100584T patent/CY1111570T1/en unknown
- 2011-09-20 DE DE201112100049 patent/DE122011100049I1/en active Pending
- 2011-09-20 BE BE2011C032C patent/BE2011C032I2/nl unknown
- 2011-09-20 LT LTPA2011011C patent/LTC1787639I2/en unknown
- 2011-09-21 LU LU91875C patent/LU91875I2/en unknown
- 2011-09-22 CY CY2011014C patent/CY2011014I1/en unknown
- 2011-09-23 FR FR11C0041C patent/FR11C0041I2/en active Active
-
2012
- 2012-04-18 CY CY20121100369T patent/CY1113028T1/en unknown
-
2018
- 2018-07-13 HU HUS1800032C patent/HUS1800032I1/en unknown
-
2019
- 2019-01-16 NO NO2019003C patent/NO2019003I1/en unknown
- 2019-07-11 NO NO2019030C patent/NO2019030I1/en unknown
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8114912B2 (en) | 2003-07-10 | 2012-02-14 | Mylan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Bronchodilating β-agonist compositions and methods |
| US8623922B2 (en) | 2003-07-10 | 2014-01-07 | Dey Pharma, L.P. | Bronchodilating Beta-agonist compositions and methods |
| JP2007500676A (en) * | 2003-07-31 | 2007-01-18 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Inhalable drugs including anticholinergics and beta receptor stimulants |
| EP2010190A2 (en) | 2006-04-21 | 2009-01-07 | CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A. | Pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers |
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1157689B1 (en) | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers | |
| US7381402B2 (en) | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers | |
| US20060257324A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurised metered dose inhalers | |
| CA2437746A1 (en) | Inhaler with means for improving chemical stability of medicinal aerosol solution contained therein | |
| EP2482799B1 (en) | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulations of formoterol and beclometasone dipropionate | |
| US20060193785A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical aerosol formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers comprising a sequestering agent | |
| US20070025920A1 (en) | Stable Pharmaceutical Solution Formulations for Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers | |
| KR20060136446A (en) | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers | |
| JP5409594B2 (en) | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulation for pressurized metered dose inhalers | |
| MXPA06009584A (en) | Stable pharmaceutical solution formulations for pressurized metered dose inhalers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20020507 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AXX | Extension fees paid |
Free format text: AL PAYMENT 20020507;LT PAYMENT 20020507;LV PAYMENT 20020507;MK PAYMENT 20020507;RO PAYMENT 20020507;SI PAYMENT 20020507 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20030416 |
|
| APBN | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2E |
|
| APBR | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3E |
|
| APAA | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS REFN |
|
| APAF | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNE |
|
| APBT | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9E |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 60137282 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20090226 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20090313 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: RENTSCH & PARTNER |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20090400818 Country of ref document: GR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2320194 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IT Ref legal event code: SPCF Ref document number: 502009901713820 Country of ref document: IT Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETASONE DIPROPIONATO/FORMOTEROLO FUMARATO(FOSTER, INUVER, ALABASTER, FORMODUAL); AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S) AND DATE(S): 64261.00.00- 64263.00.00, 20060714;037789017/M-029/M;037798016/M-028/M;037776010/M-022/M;037778014-026/M, 20070921 Spc suppl protection certif: 132009901746715 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CP Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: DIPROPIONATE DE BECLOMETASONE; FUMARATE DE FORMOTEROL DIHYDRATE; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: NL33485 20070723; FIRST REGISTRATION: DE - 64263.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: 09C0027 Filing date: 20090703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: SPCF Free format text: 0990020-0, 20080703 Spc suppl protection certif: 0990020-0 Filing date: 20080703 Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: SPCF Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BEKLOMETASONDIPROPIONAT OCH FORMOTEROLFUMARATDIHYDRAT; NAT REG. NO/DATE: DE 64263 00 00 20060714; FIRST REG.: SE 26231 20080703 Spc suppl protection certif: 09900200.L |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: CTFF Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: A COMBINATION OF BECLOMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE; REGISTERED: DE 64261.00.00 20060714; UK PL 08829/0156-0001 20071115; UK PL 08829/0157-0001 20071115 Spc suppl protection certif: SPC/GB09/030 Filing date: 20090706 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: UEP Ref document number: 419832 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: CTFF Spc suppl protection certif: CA 2009 00019 Filing date: 20090703 Expiry date: 20210714 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: AC1 Spc suppl protection certif: 300393 Filing date: 20090703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IT Ref legal event code: SPCG Ref document number: 502009901713820 Country of ref document: IT Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETASONE DIPROPIONATO/FORMOTEROLO FUMARATO(FOSTER, INUVER, ALABASTER, FORMODUAL); AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S) AND DATE(S): 64261.00.00- 64263.00.00, 20060714;037789017/M-029/M;037798016/M-028/M;037776010/M-022/M;037778014-026/M, 20070921 Spc suppl protection certif: 132009901746715 Extension date: 20210714 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: CTFG Ref document number: 200900019 Country of ref document: DK Spc suppl protection certif: CA 2009 00019 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CR Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: SOLUTION DE DIPROPIONATE DE BECLOMETASONE ET DE FUMARATE DE FORMOTEROL DIHYDRATE POUR INHALATION EN FACON PRESSURISE; REGISTRATION NO/DATE IN FRANCE: NL33485 DU 20070723; REGISTRATION NO/DATE AT EEC: 64260.00.00 DU 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: 09C0027 Filing date: 20090703 Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: SPCF Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETASONI DIPROPIONAS + FORMOTEROLI FUMARAS DIHYDRICUS; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: LT/1/08/1211/001 - LT/1/08/1211/002 20080731; FIRST REGISTRATION: DE 64261.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: PA2009003 Filing date: 20090630 Expiry date: 20210518 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: ESZA Ref document number: 419832 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: WIRKSTOFFKOMBINATION, UMFASSEND BECLOMETASONDIPROPIONAT UND FORMOTEROLFUMARATDIHYDRAT Spc suppl protection certif: SZ 21/2009 Filing date: 20090702 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: NORTON HEALTHCARE LIMITED Effective date: 20091007 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CP |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: NORTON HEALTHCARE LIMITED |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: KC1 Spc suppl protection certif: 300393 Expiry date: 20210518 Extension date: 20210713 |
|
| PLAF | Information modified related to communication of a notice of opposition and request to file observations + time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCOBS2 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: SPCG Spc suppl protection certif: 09900200.L |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: EEZF Ref document number: 419832 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: WIRKSTOFFKOMBINATION, UMFASSEND BECLOMETASONDIPROPIONAT UND FORMOTEROLFUMARATDIHYDRAT Spc suppl protection certif: SZ 21/2009 Filing date: 20090702 Extension date: 20210714 Effective date: 20100614 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: SPCR Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETASONI DIPROPIONAS + FORMOTEROLI FUMARAS DIHYDRICUS; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: LT/1/08/1211/001 - LT/1/08/1211/002 20080731; FIRST REGISTRATION: DE 64261.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: PA2009003 Filing date: 20090630 Expiry date: 20210518 Effective date: 20100827 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Owner name: CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.P.A. Free format text: CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.P.A.#VIA PALERMO, 26/A#I-43100 PARMA (IT) -TRANSFER TO- CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.P.A.#VIA PALERMO, 26/A#I-43100 PARMA (IT) |
|
| PLCK | Communication despatched that opposition was rejected |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREJ1 |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20140527 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20140527 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: MC Payment date: 20140502 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20140519 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20140527 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20140505 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20140529 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20140526 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20140506 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20140530 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20140515 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20140604 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20140526 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20140527 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20140529 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20140529 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20140602 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20140530 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Payment date: 20140505 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: SPCW Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: DIPROPIONATE DE BECLOMETASONE; FUMARATE DE FORMOTEROL DIHYDRATE; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: NL33485 20070723; FIRST REGISTRATION: 64263.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: 09C0027 Filing date: 20090703 Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: SPCW Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: DIPROPIONATE DE BECLOMETASONE; FUMARATE DE FORMOTEROL DIHYDRATE; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: NL33485 20070723; FIRST REGISTRATION: DE - 64263.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: 09C0027 Filing date: 20090703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: CTFR Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: A COMBINATION OF BECLOMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE; REGISTERED: DE 64261.00.00 20060714; UK PL 08829/0156-0001 20071115; UK PL 08829/0157-0001 20071115 Spc suppl protection certif: SPC/GB09/030 Filing date: 20090706 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: AV Effective date: 20150903 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: MM4A Free format text: LAPSE DUE TO NON-PAYMENT OF FEES Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 60137282 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: CTFL Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETASONDIPROPIONAT OG FORMOTEROLFUMARATDIHYDRAT; NAT. REG. NO/DATE: 42331 20080402; FIRST REG. NO/DATE: DE 64263.00.00 20060714 Spc suppl protection certif: CR 2009 00019 Filing date: 20090703 Expiry date: 20210518 Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP Effective date: 20150531 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MM9D Effective date: 20150518 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 419832 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150518 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20150518 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150601 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151208 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150518 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150531 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150518 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150531 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150518 |
|
| RDAF | Communication despatched that patent is revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREV1 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20150601 |
|
| RDAG | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009271 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT REVOKED |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: SPCC Spc suppl protection certif: 0990020-0 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20160129 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150518 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SI Ref legal event code: KO00 Effective date: 20160112 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: ML Ref document number: 20090400818 Country of ref document: GR Effective date: 20151208 |
|
| 27W | Patent revoked |
Effective date: 20150305 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: MP4A Effective date: 20160316 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MA03 Ref document number: 419832 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150305 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: ECNC |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: SPCF Free format text: PRODUCT NAME: BECLOMETHASONE DIPROPIONAAT + FORMOTERO FUMARAAT DIHYDRAAT; AUTHORISATION NUMBER AND DATE: 64261.00.00 20070806 Spc suppl protection certif: 2009C/021 Filing date: 20090701 Expiry date: 20210518 Extension date: 20210714 |